Settings
The Settings page allows you to customise a wide range of library-specific features. You can provide a basic configuration for components such as release workflows, validation functions, and more. If a component has multiple configurations or templates, you can find and modify them here. The component settings are stored in the ADOGRC database and can be migrated between different ADOGRC versions to preserve your settings.
The Settings page shows all library-specific component settings in the database. Depending on the ADOGRC configuration, different components can be available for configuration.
Manage Component Settings
Component settings can be imported, exported, deleted, and more.
Adjust Configurations
Some component settings offer multiple configurations, often serving as templates for charts or publications. For instance, you can add various corporate identity schemes for use in reports, or create multiple dependency modeller templates.
Other component settings feature only one configuration, typically labelled as General. In these instances, you can configure general settings for the component, such as adjusting thresholds for assessing the data actuality of objects, or configuring validation settings. While you can modify these configurations, creating or deleting them is not an option.
To adjust configurations:
Go to the Settings page.
In the catalogue on the left-hand side, find the component setting you wish to adjust, and then select the option you want:
To create a new configuration, right-click the component setting, and then click Create.
To edit a configuration, select it in the catalogue.
To delete a configuration, right-click the configuration, and then click Delete.
Import Component Settings
Component settings previously exported can be imported and stored in the ADOGRC database.
To import component settings:
Go to Settings > More options, and then click Import settings.
Click Browse and select the file you want to import. You can also drag a file from your computer to the Drag and drop files here to upload area.
Select the component settings you want to import. Alternatively, you can select Import all settings at the top to import all component settings at once.
Click Import. When prompted to continue, click Yes. The data is imported.
When the import is complete, a success message appears. Close the message to complete the process.
Behaviour if a configuration (e.g. "General") already exists in the database:
If a configuration already exists in the target library, it is overwritten with the contents of the import file.
Configurations that do not already exist in the target library are added.
Configurations that exist in the target library, but not in the import file, are not changed.
Configurations for modules are an exception. The information from both sources is combined:
If a module exists both in the source library and the target library, it is overwritten with the contents of the import file.
Modules that exist in the target library, but not in the import file, are not changed.
Export Component Settings
Component settings can be exported from the database and saved into an AXS file in the file system. This is useful to e.g. migrate chart templates which you have created to another ADOGRC version.
To export component settings:
Go to Settings > More options, and then click Export settings.
Select the component settings you want to export. Alternatively, you can select Export all settings at the top to export all component settings at once.
Click Export. The data is exported.
AI Assistant
The AI Assistant in ADONIS simplifies process creation by generating proposals based on user input. Users can provide a process description or a process name, and the assistant will generate a structured process model. The generated process can then be enhanced by automatically assigning Roles and adding descriptions to Tasks, enabling the creation of detailed and well-documented processes with ease. For details on how to configure this, please refer to the relevant section in the ADONIS Administration Help
Chart Templates
In this area you can manage chart templates.
Analysis vs. Dependency Modeller
The following templates are used when creating a so-called analysis in ADOGRC and adding charts:
Additionally, you can define templates for the dependency modeller:
Bar
Bar charts in ADOGRC visually represent objects of a specific class as bars, with an attribute dictating the length of the bars.
Templates for bar charts need to be configured in ADOGRC. The ADOGRC Administration only provides limited settings for these templates.
Open and Edit Bar Chart Template
Go to Settings > Chart Templates > Bar, and select the template you want.
For every language ADOGRC supports, you can edit the name of the template as well as the description which characterises the template.
Box-in-Box
Box-in-box charts in ADOGRC visualise hierarchies and relations between objects. They resemble a family tree. In a box-in-box chart with e. g. three layers the top layer represents the grandparents. The second layer contains the children of the grandparents, who are siblings. The third layer contains the grandchildren. The grandchildren are siblings only if they share the same parent.
Templates for box-in-box charts need to be configured in ADOGRC. The ADOGRC Administration only provides limited settings for these templates.
Open and Edit Box-in-Box Chart Template
Go to Settings > Chart Templates > Box-in-Box, and select the template you want.
For every language ADOGRC supports, you can edit the name of the template as well as the description which characterises the template.
Bubble
Bubble charts in ADOGRC display objects of a specific class as bubbles on an area defined by two axes (x-axis and y-axis), with attributes dictating the position of the bubbles on the x-axis and y-axis, and optionally the bubble size.
Templates for bubble charts need to be configured in ADOGRC. The ADOGRC Administration only provides limited settings for these templates.
Open and Edit Bubble Chart Template
Go to Settings > Chart Templates > Bubble, and select the template you want.
For every language ADOGRC supports, you can edit the name of the template as well as the description which characterises the template.
Gantt
Gantt charts in ADOGRC show objects of a specific class as bars on a timeline, with attributes dictating the start and end dates.
Templates for Gantt charts need to be configured in ADOGRC. The ADOGRC Administration only provides limited settings for these templates.
Open and Edit Gantt Chart Template
Go to Settings > Chart Templates > Gantt, and select the template you want.
For every language ADOGRC supports, you can edit the name of the template as well as the description which characterises the template.
Matrix
Matrix charts in ADOGRC display connections (matrix cells) between objects of the x-axis and objects of the y-axis. A connection can be
a relation between x-axis object and y-axis object or
an object which is connected with the x-axis and y-axis objects by relations.
Templates for Matrix charts need to be configured in ADOGRC. The ADOGRC Administration only provides limited settings for these templates.
Open and Edit Matrix Chart Template
Go to Settings > Chart Templates > Matrix, and select the template you want.
For every language ADOGRC supports, you can edit the name of the template as well as the description which characterises the template.
Dependency Modeller
The dependency modeller is a graphical means to discover and analyse dependencies between architectural objects across several architectural layers. For example, it can show which architecture objects have a direct or indirect influence on business-critical processes.
The objects and their references are visualised dynamically in a model with multiple swimlanes. Normally, ADOGRC users create the structure of this model with the dependency modeller as they go. However, when using a template, the structure is created automatically.
A template defines an entire hierarchy of object types and dependency relations. The hierarchy is based on a start modelling class and several other classes connected with relation classes. For each modelling class a layer is built, which is represented as a swimlane in the dependency modeller. The layer can be hidden, i.e. made invisible in the dependency modeller. The configuration also stores the colour selected for each layer.
Add and Configure Template
To create a dependency modeller template:
Go to Settings > Chart Templates.
Right-click Dependency Modeller, and then click Create.
In the Configuration name box, enter a name for your template, and then click OK.
Once you have created the dependency modeller template, you can start working on the configuration right away. Follow these three steps:
These steps are discussed in more detail in the following sections.
Overview
The first page of the dependency modeller template allows you to define a name and description while also providing a summary of the template.
Template name: The template's name, provided during creation, is displayed here. Adjust it as necessary.
Template description: Optionally, enter a description of the template in any language that ADOGRC supports.
Summary: Once you have selected layers and relations for the template, a summary will appear here. To view relations for a layer, on the right side of the layer, click
More.
After you have completed these settings, select page 2 from the navigation menu at the top to advance to the next page of the template.
Layers
The second page of the dependency modeller template allows you to choose a start layer and add additional layers that will be represented as swimlanes in the dependency modeller.
Start layer: First, you need to define the start layer. From the Choose start layer list, select the object type upon which the entire hierarchy of layers and relations should be based. When starting the dependency modeller in ADOGRC, one or more objects of this type must be selected so that this template can be used.
Selected layers: To create a hierarchical structure, you need to add additional layers to the template. Click Add layer and select an object type.
Change Order
You can rearrange the order of the layers:
- Drag the layer to a new position. Or, select a layer, and then click
Move to the top,
Move up,
Move down or
Move to the bottom.
Adjust Layers
Layers can be renamed, deleted, hidden, and more.
To rename a layer, on the right side of the layer, click
More, and then click Rename.
To remove a layer, on the right side of the layer, click
More, and then click Delete.
To hide a layer, to the right of the layer, click Hide layer
. This button is a toggle. Click it again to show the layer again.
To change the background colour of a layer, on the right side of the layer, click
Change background colour and choose a colour.
The start layer cannot be deleted or hidden.
After you have completed these settings, select page 3 from the navigation menu at the top to advance to the final page of the template.
Relations
The third page of the dependency modeller template allows you to add the relations that connect the layers in the template.
- Relations between layers: Define the dependency relations between layers. Choose a layer, click
More, and then Add relations, and then select the target layer and a relation. For outgoing relations, you can also use the blue circles
to the right of the layers: Click on the circle for the source layer, and then click on the circle for the target layer and select a relation.
When you add a relation, you must select a layer that is already part of the processing flow.
Suppose you have already created a template with two layers: A (= the start layer) and B. To connect
the layers, select A and create a relation to B. Whether incoming or outgoing does not matter. Now,
B will also be part of the processing flow and can be selected to create further relations. However,
if you select B instead and create a relation to A, the relation will not be processed
.
Additional Options
The following additional options are available:
To show the order in which the layers of the configuration are processed, click
Show relation processing order. This button is a toggle. Click it again to hide the order again.
To view relations for a layer, on the right side of the layer, click
More and then Relations overview.
In the Relations overview, all incoming and outgoing relations of a layer are listed.
Click
Delete to remove a relation.
After you have completed these settings, click Save. The new template is now available in ADOGRC.
ClamAV Virus Scanner
By integrating the ClamAV virus scanner into ADOGRC, files being uploaded to the ADOGRC database (documents, media files, etc.) or downloaded to your device may be checked for virus infections.
For detailed instructions on how to integrate ClamAV into ADOGRC, please refer to the chapter Enable Virus Scan for File Uploads in the Installation Manual of the ADONIS documentation.
Comments
Comments allow ADOGRC users to leave feedback and suggestions that can help improve models and objects. Users receive email notifications if they are responsible for an object or model and someone leaves a comment on it. As an ADOGRC administrator, you can define which relations indicating responsibility should trigger email notifications.
Open Comments Settings
To open the settings for comments:
- Go to Settings > Comments > General.
Notifications Configuration
The following settings are available:
Models: Select which relations should be considered for sending email notifications when new comments are created on models.
Objects: Select which relations should be considered for sending email notifications when new comments are created on objects.
Connect Center
The Connect Center is a component in ADOGRC. It provides functionality to transfer data between ADOGRC and other services that expose an HTTP interface:
between ADOGRC and its sister product ADOIT via the Integration Framework (EXT_CONNECT)
between ADOGRC and other applications such as ServiceNow via the Integration Framework (EXT_CONNECT)
Open Connect Center
To open the the Connect Center in the ADOGRC Administration:
- Go to Settings > More options, and then click Connect Center.
View Transfer Log
The transfer log ("Recent Transfers") is the first thing shown when you open the Connect Center. It shows all transfers of objects between ADOGRC and ADOIT or other applications. Whenever you synchronise objects, a new entry is added to the log.
Examine the Transfer Log
The transfer log contains the following columns of information:
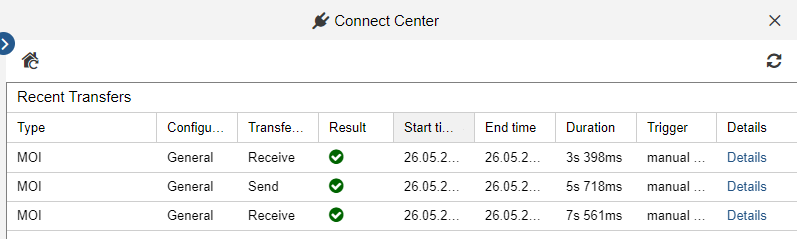
Type: Identifies the type of the transfer.
Configuration ID: The name of the configuration.
Transfer ID: The type of action executed (send or receive).
Result: Identifies whether the transfer was successful or failed.
Start time: Time stamp at the beginning of the transfer (date and time, in local time).
End time: Time stamp at the end of the transfer (date and time, in local time).
Duration: The duration of the transfer in seconds and milliseconds.
Trigger: Identifies whether the transmission was triggered manually or run automatically on a scheduled basis, and the user who performed the action.
Details: Click to open a dialogue with details about the transfer (number of created, changed and deleted objects etc.).
Start Transfer
To start transferring objects from ADOIT or other applications into ADOGRC in the Connect Center:
In the left pane, under Connectors, select the configuration you want (e.g. " ADOIT").
In the right pane, check the Properties .
Click Start Transfer.
Check Properties
The Properties pane has two tabs: General and Constants.
General
The parameters in this tab are read-only and can only be modified by editing the configuration. The following general parameters are available:
Name: The name of the configuration.
ID: The unique identifier of the configuration.
Description: A description of the configuration.
Constants
Use this tab to dynamically and temporarily set parameters for the next transfer:
- Change the values as needed, and then click Apply Constants.
The available constants depend on the selected configuration.
When you exit this view, all values will be reset to their defaults. To make the changes permanent, you need to edit the configuration and change the values there.
Manage Configurations
Configurations can be added, edited, and more. Choose one of the following actions:
Add Configuration: In the left pane, under Connectors, select the type of configuration you want ("BOC Group" or "Generic"), and then click
Create new connector configuration.
Edit Configuration: In the left pane, under Connectors, select the configuration you want, and then click
Open configuration dialog.
Delete Configuration: In the left pane, under Connectors, select one or more configurations, and then click
Delete selected connector configurations.
To find out how to configure the data connector for synchronising objects between ADOGRC and ADOIT (configuration "ADOIT"), see Configure Data Connector for the Integration Framework in ADONIS.
Connectors for other applications can only be added and configured by ADOGRC product developers or customisers.
Content
In this area you manage configuration options for the following general settings:
Change History
Changes to repository objects can be tracked in the change history. ADOGRC users can access the change history through the properties of an object.
Open Change History Settings
To open the change history settings:
- Go to Settings > Content > Change history.
Configure Change History
The following settings are available:
Activate change history: Select or clear this option to turn the change history on or off. All other options in this area will be inactive unless you select this option.
Maximum entries in the change history: Select the maximum number of entries in the change history.
Allow change history access: Select or clear this option to enable or disable access to the change history in ADOGRC. If this option is selected, you can specify which columns of the change history are shown.
Show all entries regardless of metamodel rights: By default, the complete change history of a repository object is hidden if a user has no access to one or more object attributes due to metamodel rights. Select this option to always show the complete change history, regardless of metamodel rights restrictions.
The ADOGRC application server has to be restarted if these settings are changed. Otherwise the changes will not become effective.
Document Management
Using the Document Management settings, you can configure an object type that allows ADOGRC users to upload documents into the database in order to use them in models. By default, the imported files are maintained as objects of the type Document in the Object Catalogue.
When a repository is exported for backup or migration purposes, the documents are exported as well.
Open Document Management Settings
To open the Document Management settings:
- Go to Settings > Content > Document management.
Configure Document Management
The following settings are available:
Activate Document Management: Select or clear this option to turn uploading documents on or off. All other options in this area will be inactive unless you select this option.
Class for Document Management: Select the object type to be used for managing uploaded documents from the drop-down list.
Attribute for Document Management: Select the attribute where uploaded documents should be stored.
Max file size (MB): Define the maximum allowed file size (in megabytes) for uploaded documents. The allowed maximum is 50 MB.
Allowed file types (space-separated extensions): Specify which file types users are permitted to upload as documents. Enter the file extensions separated by spaces. Default:
doc docx ppt pptx xls xlsx txt pdf rtf png jpg gif
Only file types included in the superset defined in the "Base" section of the File Management settings can be allowed here. If a file type is not listed there, it cannot be uploaded—even if added to this list.
The ADOGRC application server has to be restarted if these settings are changed. Otherwise the changes will not become effective.
Media Management
Using the Media Management settings, you can configure how ADOGRC users are allowed to upload images to the database for use in models. Uploaded images are referenced in the attributes of specific objects (Notes and Cross-References) and displayed in place of these objects in the graphical editor.
When a repository is exported for backup or migration purposes, the images are included in the export.
Open Media Management Settings
To open the Media Management settings:
- Go to Settings > Content > Media management.
Configure Media Management
The following settings are available:
Activate Media Management: Select or clear this option to turn uploading images on or off. All other options in this area will be inactive unless you select this option.
Attribute for Media Management: Select the attribute where uploaded images should be referenced.
Editable for repository objects: This option only becomes relevant in specific customising scenarios. Enabling this option and adding the attribute for the media management to the properties of a repository class enables you to set a global value for the media management attribute across all model contexts.
Max file size (MB): Define the maximum allowed file size (in megabytes) for uploaded images. The allowed maximum is 50 MB.
Allowed file types (space-separated extensions): Specify which file types users are permitted to upload as images. Enter the file extensions separated by spaces. Default:
jpg png avi tif bmp svg
Only file types included in the superset defined in the "Base" section of the File Management settings can be allowed here. If a file type is not listed there, it cannot be uploaded—even if added to this list.
The ADOGRC application server has to be restarted if these settings are changed. Otherwise the changes will not become effective.
Object Owners
In ADOGRC a user can be assigned ownership of a repository object (e.g. Applications, Processes etc.). In order to do so, the user has to be assigned as Responsible Person (property in the chapter "Organisation").
Alternatively, you can select a different relation to define ownership.
The object owner is responsible for the content of the object.
Open Object Owners Settings
To open the object owners settings:
- Go to Settings > Content > Object owners.
Configure Object Owners
The following settings are available:
Set the user automatically as object responsible after creation of objects: Select whether a user who creates an object is automatically assigned as its owner.
Relation class that should be used to define an ownership: Select a relation class as default ownership relation from a drop-down list of all ownership relations in use in the current library. This relation is then used e.g. to create ownership between an object and a user when the user creates a new object and the first option is enabled.
[OOO] When you select a relation class with the suffix [OOO], the object owner will get granted write access to the object. What type of access they had previously usually has no effect. Only metamodel rights take precedence over permissions set by an [OOO] relation.
After the assignment, ADOGRC Administrators can adjust the rights of object owners as they see fit. When the reference to the user is deleted, rights to the object are inherited as set in a superior hierarchy level (group).
Show responsible user in search results: Select this option if you want a column with the object owner to be displayed by default when search results in ADOGRC contain repository objects.
The ADOGRC application server has to be restarted if these settings are changed. Otherwise the changes will not become effective.
Corporate Identity
The corporate identity scheme (CI scheme) of an organisation can be embedded in various publications in ADOGRC (for example when printing models to PDF and creating reports).
Create one CI scheme or multiple schemes as needed. Enter your organisation's information, including the name and postal address, for each scheme. You can also upload a logo and a banner image as part of the configuration.
Add and Configure CI scheme
To create a CI scheme:
Go to the Settings page.
Right-click Corporate identity, and then click Create.
In the Configuration name box, enter a name for your CI scheme, and then click OK.
Once created, you can start working on the CI scheme right away. The following settings are available:
Name: For every language ADOGRC supports, you can edit the name of the CI scheme. Additionally, you can designate the CI scheme as the default for creating publications by selecting Use as standard.
Company details: Enter the organisation's name, postal address, and other data in the respective fields.
Corporate logo: Upload a logo that will appear in publications. If using a PNG file, ensure it has a bit depth of 24 bits or higher to avoid compatibility issues that prevent PDF reports from being generated.
Banner image: Upload a banner image that will appear near the top of the "Design & Document" start page. Select Flexible height for the banner image to allow the widget to dynamically adjust its height based on the image’s aspect ratio, ensuring the entire image is displayed without cropping. Clear this option if you are using a legacy banner image designed to be cropped at the top and bottom. Additionally, under Banner URL, you can specify a URL for every language ADOGRC supports to which users will be redirected upon clicking the banner.
Sizing Images
Images should follow these guidelines:
| Type | Width & Height | File Size | Format |
|---|---|---|---|
| Banner | With Flexible height for the banner image enabled, we recommend a width of 2000 pixels for pixel-based formats (JPEG, PNG, BMP or GIF). The aspect ratio should be between 4:1 and 16:1. With Flexible height for the banner image disabled, the recommended size is 2000 x 1000 pixels (see below the table for more information). | Less than 5MB | JPEG, PNG, BMP, GIF or SVG |
| Logo | Minimum 260 x 260 pixels. Aspect ratio approximately 1:1 for best results. | Less than 5MB | JPEG, PNG, BMP or GIF |
With the option Flexible height for the banner image disabled, banner images are cropped automatically due to varying screen sizes. This occurs mostly on wide screens, where the top and bottom are cropped. Therefore, keep the most important part of the image (e.g. logo and text) in the centre. The recommended, safe content area is approximately 2000 x 150 pixels.

Create Models/Objects
Provide guidance to ADOGRC users when they create new models and objects. You can define a set of model and object types that will be placed in the Recommendations pane of the New page.
Open Settings for the Recommendations Pane
To open the settings for the Recommendations pane:
- Go to Settings > Create Models/Objects > General.
Recommended Model/Object Types
The following settings are available:
Add Elements: Click Add to add new model and object types to display in the Recommendations pane. They will be added at the bottom of the list, in the order you selected them.
Change Order of Elements: You can change the order in which recommended elements are visualised in the Recommendations pane. Use the drag handle (
) to drag an element to a new position. Or, to the right of the element, click
More, and then click Move up or Move down.
Remove Element: To the right of the element, click
More, and then click Remove.
If no recommended elements have been configured, the Recommendations pane is not shown.
Data Actuality
Keeping your data up-to-date is crucial, and that's why we've made it easy for users to confirm the data actuality of objects in ADOGRC.
You can customise the data actuality assessment by selecting the attribute on which it should be based. Additionally, you can set thresholds that will trigger a 'yellow' or 'red' flag if an object's data actuality has not been confirmed.
Open Data Actuality Settings
To open the data actuality settings:
- Go to Settings > Data Actuality > General.
General settings
The following settings are available:
- Attribute for Data Actuality: Select the attribute on which the data actuality assessment should be based.
Global threshold
Here you can set global thresholds for assessment of data actuality. These settings apply to all object types if no class-specific values have been defined.
Number of days after which an object is marked 'yellow': Select after how many days an object is marked as 'yellow' if its actuality was not confirmed by the user responsible for this application.
Number of days after which object is marked 'red': Select after how many days an object is marked as 'red' if its actuality was not confirmed by the user responsible for this application.
Class-specific thresholds
Here you can override the global thresholds by setting individual thresholds on specific classes.
- Select after how many days objects of a specific type are marked as 'yellow' or 'red' if their actuality was not confirmed.
Excel Import
ADOGRC provides a configurable Excel interface for quick data acquisition. Via the Excel interface, you can import repository objects with their attributes and relations from an Excel file (XLS or XLSX format). For this process, the structure of the Excel file is described in an XML configuration file.
Create Configuration
An XML configuration file contains the mapping of objects from the Excel file to the ADOGRC metamodel:
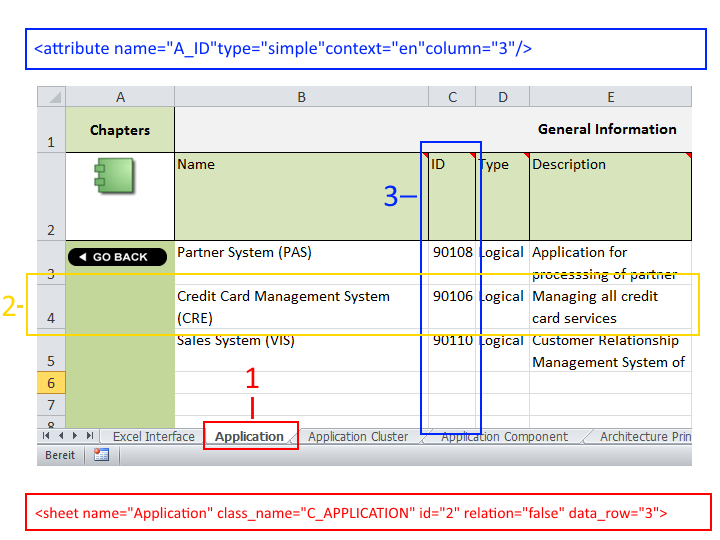
The Excel file can contain any number of sheets
Each sheet contains only objects of one type (1)
Example - XML configuration file
A configuration for a sheet could look like this:
<sheet name="Applications" class_name="C_APPLICATION" id="2" data_row="4"><sheet name>is the name of the sheet in Excel.<class_name>is the language independent name of the object type.<id>is the number of the column which uniquely identifies an object.<data_row>is the first row containing an object.Each row in the sheet contains one object (2)
Each column holds an attribute or a relation to another object (3)
Example - XML configuration file
A configuration for an attribute could look like this:
<attribute name="A_DESCRIPTION" type="simple" context="en" column="5"/><attribute name>is the language independent name of the attribute.<type>is the attribute type.<context>defines the language of the objects that are imported.<column>is the column number.A unique identifier (name, ID etc.) is needed for each object
The following attribute types can be imported: simple, date, enum, treeenumlist, enum_list, bool, relation and file_pointer
If you are using the ADOGRC Standard Application Library, one or more sample configurations will already be provided for you in the ADOGRC Administration. For every configuration, a suitable Excel file is included.
Import Configuration
In order to use a specific configuration in ADOGRC you have to import the XML configuration file first:
Go to the Settings page.
Right-click Excel import, and then click Create.
In the Configuration name box, enter a name for your configuration, and then click OK.
Click Import and upload the XML configuration file. The content of the configuration file will be displayed in the Setup box.
Click Save.
The configuration is saved. You can now import objects from any Excel file that corresponds to the configuration in ADOGRC.
Import Excel File Template
For each configuration you can import a suitable Excel file as a template.
Go to Settings > Excel Import.
Select the configuration for which you want to import a template.
Click Import Excel Template and upload the Excel file. The template's name will be displayed in the Template box.
Click OK.
The configuration is saved. The template is now available for download in the Excel import dialogue in ADOGRC. Users can download the template, capture objects in it, and then import the objects.
GRC Configuration
This section contains fundamental technical settings as well as such regarding the behaviour of certain features in the web client:
Technical Configuration: These settings are required for ADOGRC to function properly.
Configuration of ADOGRC Features: With these settings you can tailor certain aspects of the user interface to your users' needs.
Technical Configuration
These settings form the basis for ADOGRC to provide background jobs delivering critical functionality.
ADOGRC Scheduler
The Scheduler provides important background jobs for the release workflow. It can check the validity period of workflow objects, schedule them for review and prepare notifications to users among other things. To adjust the settings:
- Go to Settings > GRC configuration > Scheduler.
The following options are available:
Enable ADOGRC Scheduler: This setting turns the Scheduler on or off.
Schedule: The notation follows the cron notation: (second) (minute) (hour) (day of month) (month) (day of week). The default value is 0 0 6-23 * * ? which means the job will run every hour between 06:00 and 23:00.
Technical User: Jobs are executed within the scope of this user. To be able to run the necessary jobs, this user must have Trusted Login enabled, be defined as a technical user in the System Settings > System and have access to the repository and the workflow objects. Default is the user GRC-Scheduler.
If the system is in Maintenance Mode, the GRC Scheduler will not execute jobs.
ADOGRC Notifications
The ADOGRC Notifications Service delivers e-mail reminders to users involved in release workflows. To adjust:
- Go to Settings > GRC configuration > Notifications.
The following options are available:
Schedule: The notation follows the cron notation: (second) (minute) (hour) (day of month) (month) (day of week). The default value is 0 0/5 * * * ? which means the job will run every 5 minutes.
Language for notifications: If more than one UI language is available, it is possible to define in which language notifications are sent.
Technical User: Jobs are executed within the scope of this user. To be able to run the necessary jobs, this user must have Trusted Login enabled, be defined as a technical user in the System Settings > System and have access to the repository and the workflow objects. Default is the user GRC-Notification.
The ADOGRC Notifications Service requires that a mail server is configured. For details, see the chapter on how to configure the Email functionality.
If the ADOGRC Notifications Service is disabled or cannot run due to misconfiguration, the Scheduler will still create reminders, but they cannot be sent. This can lead to a high volume of emails being sent once the ADOGRC Notifications Service is turned on again or the configuration corrected.
General Technical User Settings
Certain background operations require a technical user in whose scope an action can run. To be able to execute these actions, this user must have Trusted Login enabled, be defined as a technical user in the System Settings > System and have access to the repository and workflow objects. Default is the user Technical. To adjust:
- Go to Settings > General technical user settings > Basic Settings.
The following options are available:
- Technical User: Jobs are executed within the scope of this user. To be able to run the necessary jobs, this user must have Trusted Login enabled, be defined as a technical user in the System Settings >System and have access to the repository and the content. Default is the user Technical .
Configuration of ADOGRC Features
These settings configure the behaviour of certain features in the web client.
General
This setting lets you configure what happens when users click the Action
button in a dashboard or table. To
configure:
- Go to Settings > GRC configuration > General.
Choose one of the three options:
Opens the Insights dashboard of the object
Opens the properties of the object
Shows the workflow menu for the object
Dashboard menus
ADOGRC displays by default two drop-down menus in the main toolbar: Inventories and Catalogs. These are dashboards for each ADOGRC object type and allow quick access to relevant information for all objects. If you do not use these dashboards, you can hide them from the user interface.
- Go to Settings > GRC configuration > Dashboard Menus.
Select which menu to hide by deselecting the checkbox. You can re-enable them at any time.
Dashboard configurations
These settings allow you to adapt the tabular dashboards ADOGRC provides to give your users the information they need. You can add or remove columns and configure the way these columns are displayed. These settings are available for Inventories, Catalogs and the My ... dashboards.
To configure a dashboard:
Go to Settings > GRC configuration > Dashboard configurations.
Select a dashboard from the drop-down menu.
When you are done with the configuration, click the Save button at the top.
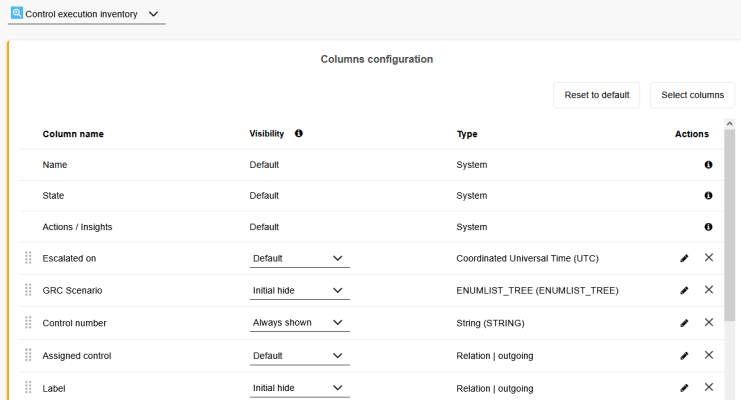
The following options are available to configure a dashboard:
Add or Remove Columns
To provide users with all necessary information they need at a glance, you can add columns to a dashboard:
Click the Select columns button.
Select or de-select a column in the list.
Optional: Quickly find columns by typing the name into the search bar.
Click Apply to save the new selection.
System columns cannot be moved or removed but you can view them in the Select columns dialog, on the System / Special tab.
Custom attributes created in the new Properties Management can be added as special columns allowing to further personalize dashboards.
Edit Column
You can configure the names of columns and adjust how they are displayed in the dashboard. Changing the names of columns affects only the names in that specific dashboard, it does not rename the attribute. To change the name of a column:
Click the Pen
icon of the column you want to edit.
In the dialog, change the name of the column in all available languages.
Optional: Click the Reset button to revert to the last saved state.
Optional: Click the Reset to default button to revert to the names ADOGRC is shipped with.
On the Options tab you can select the defaul width of a column. Users will still be able to change the width in the dashboard. You can also set the Visibility options for this column (see next section).
Set Visibility Options
With this setting, you can configure the way columns are displayed in the dashboard. To configure, select one of the options from the drop-down menu in the Visibility column or open the Edit column dialog and switch to the Options tab.
There are three options available:
Default: The column will be shown as long as there is enough space on the screen.
Initial hide: The column will not be shown when opening the dashboard but can be added by the user at any time.
Always show: This setting gives a column priority: If there is not enough space on the screen, columns with the Default settings will be hidden to make room for columns with the Always show setting.
Additional Options
In addition to the settings above you can:
Quickly remove columns by clicking the X icon in the overview.
Move a column by dragging it up or down with the handle
symbol on the left.
Revert an entire dashboard to its initial state with the Reset to default button.
System columns cannot be moved or removed.
HTML Publishing
By default, the search page will be displayed as the start page of an HTML publication, including embedded corporate identity elements. You can configure a custom start page instead. To do so, upload a single HTML page.
The uploaded file must contain all images, scripts, style information etc. inline, or download it from a place in the web. To include images inline within the HTML page, they have to be embedded base64-encoded.
Open HTML Publishing Settings
To open the HTML publishing settings:
- Go to Settings > HTML Publishing > General.
General
The following settings are available:
Disable custom start page: Choose whether to show the uploaded file in HTML publications. This option is useful if you want to temporarily disable a custom start page.
Custom start page - file name: Click Browse and upload the HTML page that you want to use.
Custom start page - file content: The content of the uploaded HTML file is displayed here.
Integration - Configuration
The Integration Framework is a generic ADOGRC extension that can be used to create and configure adapters connecting to any kind of third-party tool that exposes an HTTP interface which allows fetching of data.
In this area you manage general configuration options for the Integration Framework.
A detailed description of this functionality is beyond the scope of this manual. If you have questions, please contact your ADOGRC consultant.
Integration - Data Connectors: ADOIT
ADOGRC offers synchronisation of objects between ADOGRC and ADOIT.
In typical scenarios, certain objects (such as
Application Components in
ADOIT or
Processes and
Roles in ADOGRC ) are
only maintained in one of the two products. By synchronising these objects, they are made available
in the respective other product:
Application Components will be imported as
Applications in ADOGRC
Processes and
Roles will be imported as
Business Processes and
Business Actors in ADOIT
A REST API is used for the communication between the products.
The availability of this feature depends on the licence.
Configuration
The configuration is carried out via the Integration Framework. If you are using ADOGRC 14, you can synchronise objects with the following ADOIT versions:
- ADOIT 15.1.16 or higher | ADOIT 16.0.12 or higher | ADOIT 17 or higher
Instructions on how to set up the synchronisation are covered in the following sections here in the Administration Help.
Synchronisation
Synchronisation can be triggered manually (in the Connect Center ). It is also possible to configure the synchronisation to run automatically on a scheduled basis.
Compatible Application Libraries
The synchronisation of objects between compatible ADOGRC and ADOIT is supported without further customising effort if the default libraries delivered with the product are used:
On the ADOGRC side:
- the ADOGRC Standard Application Library
On the ADOIT side:
- the ArchiMate Application Library
Please contact your BOC consultant for further assistance if other application libraries are in use. This includes default libraries with changes in the metamodel, or other specific libraries.
Setting Up Synchronisation via the Integration Framework
To synchronise objects between ADOGRC and ADOIT via the Integration Framework, you have to define settings in BOTH products.
First, enable access to the REST API on the ADOIT side so that ADOGRC can retrieve data from there:
Next, create a technical user on the ADOGRC side:
Then you can configure the data connector that will be used to connect to ADOIT on the ADOGRC side:
Synchronisation is now set up. Depending on the Application Library and the product configuration, you may need to configure additional settings:
Once you have completed the setup process, it's time to provide the right people access to the synchronisation features in ADOGRC:
These steps are explained in the following sections.
The procedure described here ONLY applies to importing EA elements from ADOIT into ADOGRC. If you want to import BPM elements from ADOGRC into ADOIT, set up the synchronisation as described in the ADOIT Administration Help.
The Apache Tomcat web servers and the application servers of BOTH products have to be restarted if these settings are changed. Otherwise the changes will not become effective.
Activate Access to the REST API in ADOIT 
First, you need to enable access to the REST API in ADOIT (as described in the ADOIT Help). Synchronisation via the Integration Framework requires you to configure one of the following authentication methods:
Basic Authentication
OAuth 2.0 Authentication using the Client Credentials Flow
Token Based Authentication
The Integration Framework does not support OAuth 2.0 authentication using the Authorization Code Flow, OIDC authentication and JWT authentication.
The user in whose context requests should be executed does NOT need access rights to the component "Administration Toolkit".
You need to activate at least the following REST scenarios for the authentication method you have chosen:
Repository read APIs
Repository write APIs
Metamodel read APIs
Create Technical User 
Configuring a data connector for the Integration Framework requires a technical user. If you set up a periodic synchronisation, it will be performed in the context of this technical user.
To create the technical user in the ADOGRC Administration:
Go to the Users page and click New User.
Enter the following data:
Name: "Technical_ManagementOfficeIntegration" (and a password of your choice)
Trusted Login: Yes
User groups: This user belongs to the default group.
System roles: If release workflows are licensed, map the technical user to the “Administrator” roles (Document Release Workflow and Model Release Workflow).
Repository: Only (!) assign the repository to the user into which the EA elements from ADOIT should be imported.
Trusted Login can only be enabled after the user has been created. Complete the user creation by clicking Create, then edit the user once more to enable Trusted Login.
Configure Data Connector for the Integration Framework in ADOGRC 
Now, you need to configure the data connector that will be used to connect to ADOIT. You have two options:
Quick Setup: Quickly configure the data connector with default settings. Available when basic authentication or OAuth 2.0 authentication is used for the REST API in ADOIT.
Custom Setup: Required if token-based authentication is used for the REST API in ADOIT. Or, if you want to customise settings, such as selecting the language for data transmission or enabling periodic synchronization.
Data Connector: Quick Setup
Would you like to quickly set up the data connector in ADOGRC using the default settings? This option is available if the REST API in ADOIT uses basic authentication or OAuth 2.0 authentication. Proceed as follows:
- Go to Settings > Integration - Data Connectors > ADOIT.
The quick setup has 2 pages:
These pages are discussed in more detail in the following sections.
Connect
On the first page of the quick setup, configure the following settings:
Source Product URL: Enter the URL where ADOIT is available.
Authentication Method: Select the authentication method used for the REST API in ADOIT:
Basic Authentication: The following parameters must be specified:
Username: Enter the name of the user in whose context REST API requests should be sent in ADOIT.
Password: Enter the corresponding password. Will be stored in encrypted form.
OAuth 2.0: The following parameters must be specified:
Client ID: Enter the ID of the client system as specified in the ADOIT Administration in the Client Data form.
Client Secret: Enter the Secret to use for client authentication as specified in the ADOIT Administration in the Client Data form. Will be stored in encrypted form.
Scope: Enter the name of the Scope as specified in the ADOIT Administration on the OAuth 2.0 tab.
Test Connection: Click this button to test the connection. If the test is successful, you will proceed to the next step. If the test fails, review the details entered on the Connect page and verify the REST API settings in ADOIT.
Configure
On the second page of the quick setup, configure the following settings:
- Choose Roles: Select the system roles allowed to synchronise data.
Technically, this means the system role Connector for ADOGRC and ADOIT will be assigned to the chosen system roles. Users with these system roles will be able to open the Connect Center in ADOGRC and import objects from ADOIT into ADOGRC. However, they cannot modify the connector configuration in the Connect Center unless they also have the Module: Connect Admin module assigned.
Source Repository: Select the repository in ADOIT that holds the objects that should be imported into ADOGRC.
Select technical user: Select the technical user you created in ADOGRC, i.e. "Technical_ManagementOfficeIntegration" (see Create Technical User).
Setup: Click this button to save your settings and complete the quick setup.
Data Connector: Custom Setup
If the REST API in ADOIT uses token-based authentication, or if you want to customise settings, a custom setup is required.
Completing the quick setup first is the recommended approach if the REST API in ADOIT uses basic authentication or OAuth 2.0 authentication and you want to fine-tune specific settings. This ensures all necessary configurations are in place, making further refinements easier.
Proceed as follows:
Go to Settings > More options, and then click Connect Center.
In the left pane, under Connectors, select the configuration " ADOIT", and then click Open configuration dialog
.
Edit the settings on the General Configuration, Technical Settings, Data Synchronization and Constants tabs.
Click OK when you have completed the settings.
General Configuration
Edit the following settings on this tab:
Name: The name of the configuration. Usually, the default value does not need to be changed.
ID: The unique identifier of the configuration. Usually, the default value does not need to be changed.
Description: (Optional) A description of the configuration.
Connector type: Must be set to BOC Group.
Enabled: Select this check box to enable the data connector.
Technical Settings
Edit the following settings on this tab:
- URL: Enter the URL where ADOIT is available.
Example
You are configuring ADOGRC. ADOIT 17.3 is the other product. You are running the ADOIT web application on a machine with the IP 10.2.100.62. The URL should look like this:
"http://10.2.100.62:8000/ADOIT17_3"
Authentication Type: Select the authentication method you have configured in ADOIT for access to the REST API:
Basic: For basic authentication. In addition, the following parameters need to be adjusted:
Username: Enter the name of the user in whose context REST API requests should be sent in ADOIT.
Password (encrypted): Enter the password of the user in whose context REST API requests should be sent in ADOIT. The password must be encrypted with an encryption tool which can be found in the directory "03 Web Application\02 Tools\02 Password Encryption Tool" in the installation package.
ADO: For token based authentication. In addition, the following parameters need to be adjusted:
Key: Enter the Key (for authentication by target system) that you defined in the ADOIT Administration on the Tokens tab, e.g. “boc.rest.key.mfb.ManagementOfficeIntegration”.
Secret: Enter the Secret (for authentication by target system) that you defined in the ADOIT Administration on the Tokens tab. Copy the 512 characters long key directly from the ADOIT Administration. Both values must match exactly.
OAuth 2.0: For OAuth 2.0 authentication. In addition, the following parameters need to be adjusted:
Grant Type: Must be set to Client Credentials.
Client ID: Enter the ID of the client system that you specified in the ADOIT Administration in the Client Data form.
Client Secret (encrypted): Enter the Secret to use for client authentication that you specified in the ADOIT Administration in the Client Data form. The password must be encrypted with an encryption tool which can be found in the directory "03 Web Application\02 Tools\02 Password Encryption Tool" in the installation package.
Client Authentication: Must be set to Send client Credentials as Basic Authentication header.
Token URL: Enter the Redirect URI that you specified in the ADOIT Administration in the Client Data form.
Scope: Enter the name of the Scope that you specified in the ADOIT Administration on the OAuth 2.0 tab.
Technical User: Add the technical user you created, i.e. “Technical_ManagementOfficeIntegration” (see Create Technical User). If you enable periodic synchronisation, it will be performed in the context of this user.
Periodic synchronisation: (Optional) Here you can set up periodic synchronisation of objects between ADOGRC and ADOIT via the Integration Framework. During periodic synchronisation, EA elements are imported from ADOIT into ADOGRC. Adapt the following parameters:
Synchronise periodically: Select this check box to activate periodic synchronisation.
Daily/CRON Expression: If periodic synchronisation is enabled, you can define the point in time at which the objects are synchronised here. You can choose when to do this in one of two ways:
Daily: In the Synchronisation Time box, define the point in time at which the objects are synchronised daily.
CRON Expression: Use a CRON expression to specify how often objects should be synchronised.
Data Synchronisation
Edit the following settings on this tab:
- lang: Specification of the language in which the data is transmitted, e.g. "de" for German and "en" for English. Available languages depend on the on the Application Library and the licence.
Objects can only be transmitted in one language.
Constants
Edit the following settings on this tab:
adoitRepositoryID: The ID of the repository in ADOIT that holds the objects that should be imported into ADOGRC.
importFolderPath: The name of the object group in ADOGRC that contains the imported objects. This group will be created automatically if it does not already exist.
obsoleteFolderID: The ID of the object group in ADOGRC that contains objects that could not be deleted.
In general, imported objects are deleted during synchronisation if they have been removed from ADOIT in the meantime.
However, if relations have been added to the imported objects in ADOGRC, or they are being used in models in ADOGRC, they are not deleted. They will be moved to the "Obsolete objects" folder instead. An exception to this rule is the relation Responsible person. Although a relation of this type was added in ADOGRC, imported objects will be deleted anyway.
- pageSize: The number of objects that are imported from ADOIT at once.
This parameter may be used to avoid performance and out-of-memory problems. For example, set the value to "100" so that 3,000 objects are transferred in 30 blocks of 100 objects each.
Import System Role and Assign Users 
Are you using the default libraries delivered with the product? Then import the Management Office Integration system role in the ADOGRC Administration now and assign all users to it, excluding technical users and those designated to perform the synchronisation. This will prevent your users from changing imported objects which should be maintained in ADOIT.
Import System Role
To import the Management Office Integration system role in the ADOGRC Administration:
Go to System Roles > More options, and then click Import system roles.
Click Browse and select the system roles file. The respective file
<date> - <library name> - MOI Role.axrcan be found in the folder “04 Sample Data/Roles“ in the installation package. You can also drag the file from your computer to the Drag and drop files here to upload area. Then, click Next.Select the system role Management Office Integration. Then, click Next.
Make sure that the option Including metamodel rights is activated. Do not change the other settings. Then, click Import. The system role is imported.
When the import is complete, a success message appears. Close the message to complete the process.
Assign Users to System Role
To assign users to the Management Office Integration system role in the ADOGRC Administration:
Go to the System Roles page.
In the System roles catalogue on the left side, select the Management Office Integration system role.
Click Add members and add user groups or individual users from the user catalogue. Then, click Add.
Click Save.
The users are assigned.
Do NOT assign the following users to the system role Management Office Integration:
Technical users or their user groups (= default group)
Users tasked with performing the synchronisation or their user groups
Effects of the System Role
The Management Office Integration system role has the following effects:
- users are not allowed to create Applications, and only have read access to their properties
Set up Access to the Synchronisation of Objects for Users 
By assigning two modules in the ADOGRC Administration, you can provide the right people access to the synchronisation features in ADOGRC:
Go to Settings > System settings > Modules.
Assign the following module to system roles you want to allow access to:
- Connector for ADOGRC and ADOIT
Done! All users with the relevant system roles can now import objects from ADOIT in ADOGRC.
Users with access to these web modules are tasked with performing the synchronisation and must NOT be assigned the restrictive system role "Management Office Integration" (see Import System Role and Assign Users), as otherwise they will not be able to perform the synchronisation correctly.
MCP Services
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) server in ADOGRC provides a standardised mechanism for delivering context specific information in scenarios using AI systems such as large language models (LLMs). This allows information and capabilities to be transferred smoothly between AI systems and ADOGRC, reducing the need for complex integration infrastructure.
For general information on MCP, see the Wikipedia article and the official MCP documentation.
To utilise this capability, an agent is required that has access to the ADOGRC MCP server and is integrated with an AI system (usually an LLM). This agent is typically developed or provided by the customer. Context-specific data access within ADOGRC is enabled via tools that expose defined functionalities, which the agent can discover and execute upon instruction from the AI system.
Preconfigured Tools
In ADOGRC 14.2, the following tools are preconfigured, allowing users to interact with the MCP server using natural language:
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
_getRepositories | Returns a list of all repositories. |
GetRepositoryLanguages | Retrieves all available languages, including the primary language (e.g., "search for all supported languages in ADONIS"). |
Search | Searches a repository for models and objects by name and description, optionally filtered by type (e.g., "search for all objects containing payment in the name"). |
getObjectDetails | Retrieves properties of a repository object (e.g., "get details for the object Payments System"). |
GetModelDetails | Retrieves properties of a model (e.g., "get details for the model Application Process"). |
getModellingObjectDetails | Retrieves properties of a modelling object inside a model (e.g., "get details for the task 'Check application documents' inside the model Application Process"). |
GetClasses | Lists all object types from the metamodel (e.g., "list all classes"). |
GetModelTypes | Lists all model types (e.g., "list all model types"). |
GetAllSavedQueries | Searches a repository and returns a list of all saved queries (e.g., "list all my stored searches"). |
ExecuteSavedQuery | Executes a saved query in a repository and returns the results (e.g., "execute the saved query Expiring Technologies"). |
All tools operate in the context of the user account in ADOGRC, under which the REST requests to the MCP server are executed (see Activate Access to the REST API). For example, if this account only has access to certain repository areas, not all elements can be found.
Additional tools can be configured based on the concrete scenario by BOC Solution Engineers as part of customising projects. Tools in ADOGRC can be configured to use any functionality provided by the ADOGRC REST API.
Enable MCP Server
Before adapting your agent, you must activate access to the MCP server in ADOGRC. The necessary instructions for doing so are provided here in the Administration Help:
Agent Setup
Once access to the MCP server is enabled, a local agent is required to establish communication between the LLM and ADOGRC. The agent is an independent component that:
Implements the MCP protocol
Is configured with the appropriate credentials and endpoints
ADOGRC does not provide this agent out of the box. However, a reference implementation in Python is available via the BOC Developer Portal.
LLM Subscription and API Key
Integrating with an LLM typically requires a subscription to the chosen LLM provider (e.g., OpenAI). The provider’s API key must be securely stored and referenced by the agent to allow it to forward requests and receive processed model context data.
Use MCP Services
For further guidance on using the MCP services in ADOGRC, please refer to the BOC Developer Portal, especially:
Activate Access to the REST API
First, you need to enable access to the REST API in ADOGRC (as described in REST API). The MCP Services require you to configure one of the following authentication methods:
Basic authentication
OAuth 2.0 authentication
The MCP Services do not support OIDC authentication, JWT authentication and token based authentication.
The user in whose context requests should be executed does NOT need access rights to the component "Administration Toolkit".
You need to activate at least the following REST scenarios for the authentication method you have chosen:
Repository read APIs
Repository write APIs (if write access is desired)
Repository search APIs
Depending on the specific use case, additional REST scenarios may need to be activated.
Activate the MCP Services
With access to the REST API enabled, all that needs to be done is to activate the MCP services. Proceed as follows:
Go to Settings > MCP Services > General.
Select Enable MCP Services to activate the feature.
Click Select repository and select the repositories for which the MCP Services should be enabled.
Done! The MCP server can be used now.
Configure IP Restrictions for the MCP Server
If you want to limit which IPs can access the MCP server, you need to adapt the Security settings in the ADOGRC Administration:
Go to Authentication > More options, and then click Security Settings.
Switch to the MCP tab.
Adapt the following setting:
- MCP IP Restrictions: This setting is optional. You can restrict the IP addresses that are allowed to access the MCP server (see Configure IP Restrictions for more information).
MCP IP restrictions apply together with the IP restrictions configured for REST API communication via Basic Authentication or OAuth 2.0. For details, see:
"Basicauth IP Restrictions" in the section Enable Basic Authentication for ADOGRC
"IP constraints" in the section Configure Settings for OAuth 2.0
Model Release Workflow
ADOGRC provides a model release workflow management system which allows to formalise model release and versioning. During the release process contributors carry out different tasks depending on their system roles.
The availability of the model release workflow depends on the licence.
Set up Access to Model Release Workflow
You can use the default configuration of the model release workflow or a user-defined configuration.
Default Configuration
To use the default configuration, add users to the following system roles depending on their task in the release process. These are sub roles of the system role "Model Release Workflow":
Modellers create and submit models to review. They can also create new versions of models which have already been released in order to adapt them.
Reviewers perform methodical reviews [system role reviewer (methodical)] and business reviews [system role reviewer (business)] of the submitted models.
Administrators can execute all transitions. They are responsible for the maintenance of the release process. Only Administrators can manually archive models (when a new version of a model is released, the previous version is archived automatically).
Afterwards the model release workflow is ready for use.
User-Defined Configuration
To use a user-defined configuration, the following steps are necessary:
Configure the model release workflow. Add new system roles (e.g. A, B, C, …) on the Configure Roles page.
Add users to the appropriate system roles depending on their task in the release process.
Afterwards the model release workflow is ready for use.
Please refer to the section Manage System Role Members for details on how to assign system roles to users.
Configure Model Release Workflow
To configure the model release workflow:
- Go to Settings > Model Release Workflow > General.
The model release workflow configuration wizard has 5 pages:
These pages are discussed in more detail in the following sections.
Configure Mapping
The first page of the model release workflow configuration wizard allows you to select model types, model references and attributes.
Do not use metamodel rights to restrict access to attributes and relations configured here, as these attributes and relations are required for the model release workflow to work.
You can view and edit the following data:
Main Configuration
- In the Configuration name area, edit the language-specific names of the model release workflow for all languages ADOGRC supports. These names are visible on the user interface, e.g. in the state filter.
Model Type Selection
- Select the model types that should be available for use in the model release workflow.
When you configure a specific transition, you can specify for which model types that transition is enabled. However, you can only select from the model types made available here.
Version Configuration
- Define the minor version format and the major version format which is assigned to models during versioning.
Prolongation Configuration
To turn the prolongation functionality on or off, select or clear the Active check box.
In the Daily validity check at (hh) box, type or select the hour of the day (in 24-hour time format) when the validity of all versioned models is automatically checked on the ADOGRC application server. The default setting is each night at 1:00 AM local time.
Version History Functionality
To turn the Version history functionality on or off, select or clear the Active check box.
Select the Maximum entries in the version history. When this sum is reached, the oldest entries are removed from the table.
Process Responsible Functionality
To turn the Process responsible functionality on or off, select or clear the Active check box.
Select the Process owner, the Process manager, the Methodical reviewer and the Process analyst/designer relations. These relations represent the stakeholders who are responsible for a process.
The relations Additional responsible 1, 2 and 3 allow you to define up to three additional relations representing process representatives.
If process responsible functionality is activated, you can define various conditions, checks and actions which are otherwise not available. You may e.g. specify that only models with a Process owner defined in their properties can transition to a new state.
After you have completed these settings, select page 2 from the navigation menu at the top to advance to the next page of the model release workflow configuration wizard.
Configure States
The second page of the model release workflow configuration wizard shows all states in the workflow, along with their details. You can edit and create new states.
The following options are available:
Edit State: To the right of the state, click
More, and then click Edit. Now you can configure the state.
Copy State: To the right of the state, click
More, and then click Copy. Now you can configure the state.
Delete State: To the right of the state, click
More, and then click Delete.
Add State: Click Add new state. Now you can configure the state.
Change Order of States: Use the
icon with three horizontal lines to the left of a state to drag it to a new position.
You can edit some status details inline directly on the Configure States page, namely Type, Icon, and Colour.
Edit or Add Transition State
When you add or edit a state on the Configure States page, a form will appear. You can view and edit the following data:
Language Independent Name
- A language-independent name that uniquely identifies the state is applied automatically based on the enumeration values of the State attribute.
Language-Specific Names
- Edit the language-specific names for all languages ADOGRC supports. These names are visible on the user interface.
Icon
- Edit the state icon directly in the text box. If ADOGRC is installed, you can find a full list of icons by adding /fonts/awesome/icon-index.html to the URL of ADOGRC, e.g. http://localhost:8000/ADONIS17_2/fonts/awesome/icon-index.html. The keyword "axw-fa " (space after axw-fa) has to be added as a prefix to the icon name.
Colour
- Edit the colour of the state icon and the colour of the state in pie charts. Click the colour circle and choose a colour, or enter a specific Hex colour value manually.
Type
Select the predefined state type that corresponds to this state. State types include logic for the interplay with the process release workflow, validation checks etc. Each state type bundles certain release workflow behaviours.
"Draft": Select if the state represents draft versions of models. In models with a state of the state type "Draft" it is ensured that the contained versioned objects are automatically present in the latest released version or draft version. Contained objects are updated when there is a new draft version or when there is a new released version.
Example
When you create a new draft version of a Process, the new object replaces the original object in all Process Landscapes that are in the state "Draft".
"Review": Select if the state represents models that are currently being reviewed. In models with a state of the state type "Review" it is ensured that the contained versioned objects are automatically present in the latest released version.
"Released": Select if the state represents released models (released, valid etc.). In models with a state of the state type "Released" it is ensured that the contained versioned objects are automatically present in the latest released version.
"Archived": Select if the state applies to archived models. The state of the contained versioned objects does not change in models with a state of the state type "Archived". Archived objects remain archived and are not replaced by new released versions.
State as Model Group
Select Represent state as model group to have models cycle through folders with the name of the current state during versioning. All other options in this area are inactive unless you select this check box.
From the Use model group of the referenced state list, you can reference another state. Models in the current state will now appear in the model group of the referenced state.
Click Custom group name to specify a custom name for the model group. Enter a language-specific name for every language ADOGRC supports.
Example "Represent state as model group"
Models in the states "Under methodical review" and "Under business review" should appear in the same custom model group ("Under review"). To do this, follow these steps:
State "Under methodical review"
Activate the option Represent state as model group.
The Custom group name is "Under review".
"Under business review"
Activate the option Represent state as model group.
From the Use model group of the referenced state list, select the state "Under methodical review".
After you have completed these settings, select page 3 from the navigation menu at the top to advance to the next page of the model release workflow configuration wizard.
Configure Roles
The third page of the model release workflow configuration wizard shows all system roles specific to the release workflow (= RWF roles or release workflow roles). You can edit and create new roles.
Add the users to the appropriate system roles depending on their tasks in the release process.
The following options are available:
Edit Role: To the right of the role, click
More, and then click Edit. Now you can configure the role.
Copy Role: To the right of the role, click
More, and then click Copy. Now you can configure the role.
Delete Role: To the right of the role, click
More, and then click Delete.
Add Role: Click Add new role. Now you can configure the role.
Allowed to Create New Models: Select Allowed to create new models so that users with a specific role can create models of those model types for which the model release workflow is enabled. Note that this setting only applies to model types that are part of the release workflow and has no effect on other model types.
Edit or Add Role
When you add or edit a role on the Configure Roles page, a form will appear. You can view and edit the following data:
Language Independent Name
- Enter a language-independent name that uniquely identifies the system role.
Language-Specific Names
- Edit the language-specific names for all languages ADOGRC supports. These names are visible on the user interface
After you have completed these settings, select page 4 from the navigation menu at the top to advance to the next page of the model release workflow configuration wizard.
Configure Rights
The fourth page of the model release workflow configuration wizard allows you to set access rights to models in the model release workflow depending on system role and state.
Access Rights for Models
- Select access rights to models in each state from the corresponding drop-down lists.
You can define access rights for every release workflow role and for users without a release workflow role ("All others").
Users without a release workflow role should not have write access to release workflow models, because they can use it to override the mechanisms of the release workflow.
The following types of access are available:
Read: The user can access this element but is not allowed to make changes.
Write: The user may use, modify, save, and delete the element as they want.
Read Models with Translation Option: The user may not modify the model in structure and size, but they may translate existing attribute values into other content languages.
No Access: This element is not available for the user (it is invisible for them in the various lists and catalogues).
Default Rights (Inherited): Permissions for models as set at the level of user groups or directly at the user level apply. See Rights for details.
After you have completed these settings, select page 5 from the navigation menu at the top to advance to the next page of the model release workflow configuration wizard.
Configure Transitions
The fifth page of the model release workflow configuration wizard lists all transitions in the workflow. For every transition, the source state of the model before the transition and the target state of the model after the transition is shown. You can edit and create new transitions.
The following options are available:
Edit Transition: To the right of the transition, click
More, and then click Edit. Now you can configure the transition.
Copy Transition: To the right of the transition, click
More, and then click Copy. Now you can configure the transition.
Delete Transition: To the right of the transition, click
More, and then click Delete.
Add Transition: Click Add new transition. Now you can configure the transition.
Change Order of Transitions: Use the
icon with three horizontal lines to the left of a transition to drag it to a new position.
Edit or Add Transition
When you edit an existing transition or add a new transition, a dialogue window containing the following tabs opens:
These tabs are discussed in more detail in the following sections.
General Settings
The General Settings tab contains the following settings:
Edit the language independent name and the language-specific names of the transition directly in the respective text fields.
Select whether ADOGRC should create a menu item for the transition on the user interface.
When you execute a transition in ADOGRC, the state icon of the target state is displayed in menus and in the "Control & Release" dashboard. To replace the state icon with another icon, edit the Icon (overrides the target state icon) directly in the respective text field. If ADOGRC is installed, you can find a full list of icons by adding /fonts/awesome/icon-index.html to the URL of ADOGRC, e.g. http://localhost:8000/ADONIS17_2/fonts/awesome/icon-index.html. The keyword "axw-fa " (space after axw-fa) has to be added as a prefix to the icon name.
Configure States
Configure the states of the transition:
Select source state and target state lets you select one or more source states and a target state.
Initial transition means that the status of a model which has no source state changes to the initial model release workflow status (e. g. "Draft") when this transition is carried out.
Transition is valid in each state means that this transition can be carried out regardless of the source state of the target model.
When a transition is configured to be an initial transition, notifications are disabled.
When a transition is configured to be valid in each state, all actions are disabled and reset except:
History settings
Show success message for transition
System Transition
For certain scenarios it is necessary that transitions correspond to a certain type. Each system transition brings some logic with it. At the moment, ADOGRC supports the following types of system transitions:
No entry: This setting is disabled. The transition is not a system transition.
Reminder: When the validity of the model should be rechecked, reminders are sent to the responsible user(s).
noteWhen a transition is configured as a Reminder system transition, the Reminder tab will be enabled, allowing you to further configure the reminder details.
Accept: When the "Valid from" date has been reached, the state of the model changes to "Valid".
Invalidate: When the "Valid until" date has been reached, the state of the model changes to "Invalid".
Vote: Activate this setting if the transition represents a vote.
noteWhen a transition is configured as a Vote system transition, the Voting tab will be enabled, allowing you to further configure the voting process.
Prolongate: Activate this setting if the transition represents a prolongation action (= extend validity period).
noteWhen a transition is configured as a Prolongate system transition, you can define various actions which are otherwise not available.
The system transitions Reminder, Accept and Invalidate are executed automatically without user interaction. Each night at 1:00 AM local time the ADOGRC application server checks whether models meet the specified conditions. If yes, the system transition is executed.
Conditions
The Conditions tab contains the following settings:
RWF Roles Which Are Allowed to Execute this Transition
- Define the system roles which are allowed to execute this transition.
You can only select from the system roles configured for the release workflow on the Configure Roles page.
Model Type Selection
- Define for which model types this transition is enabled.
You can only select from the model types made available for the model release workflow in the Model Type Selection area on the Configure Mapping page.
Process Responsibles Who Are Allowed to Execute the Transition
- In this area you can specify that only process responsibles can execute this transition. The user must also have the appropriate system role.
You can combine multiple conditions. The transition can only be executed if all conditions are met (logical AND operator).
Checks
The Checks tab contains the following settings:
Select the Do not execute any check action check box to skip all checks, or clear it so you can define various checks to be carried out before the transition is executed.
Select the Do not allow empty models check box to require the model to contain at least one object before the transition can be executed, or clear it to allow transitions with empty models.
Process Responsible
In this area you can specify that only models with a process responsible defined in their properties can transition to the target state. You can further specify whether a process responsible has to be user based (a referenced User object), role based (a referenced Role object) or can be both.
If Warn if assigned roles are available for reader assignment is activated, ADOGRC displays a warning when the transition is executed, and the following condition is fulfilled: A Role object that is used in the model release workflow as a process responsible is Available for reader assignment (property in the chapter "General information"). The user cannot execute the transition.
Incoming References
If Do not allow incoming references is activated, a dialogue will appear when the transition is executed and the model contains incoming references. The transition cannot be executed by the user.
If Inform if incoming references exist is activated, a dialogue will appear when the transition is executed and the model contains incoming references. The transition can be executed regardless by the user or aborted.
Outgoing References
If Warn if subordinated models are not released is activated, a warning appears when the transition is executed, and the following condition is fulfilled: The model contains at least one Subprocess that references a Business Process Diagram which is not released. The transition can be executed regardless by the user or aborted.
Select Include referenced models so that referenced models will also transition to the target state. This is e.g. the case when a model is referenced in a Business Process Diagram as a subprocess.
If this option is activated, you have to select a strategy for handling referenced models in case of conflict. Include all or none means that transition will only be executed if all referenced models have the correct state for the transition. Include with best effort means any referenced models that cannot be transitioned will be skipped and the transition will be allowed for the rest of the models. User decides lets the user decide between the following options: Do not include referenced models, Include all or none or Include with best effort.
If Do not allow if validity period is invalid is activated, the transition cannot be executed if the end of the validity period is in the past.
If Do not allow if there is no access to the target model group is activated, the transition can only be executed if the user has write access to the group where the model will appear after the transition.
If show success message for checks is activated, a message box will appear when all checks have been performed successfully.
Checks
- In the Checks area, you can configure which checks are carried out when models are submitted to review. In addition, you can define the behaviour when the check shows that the models are not valid: either the transition may not be executed at all (Block transition), or merely a notification appears (Confirm transition).
Actions
The Actions tab contains the following settings:
Select the Do not execute any execute action check box to skip all actions, or clear it so you can define various actions to be carried out after the transition is executed.
You can define whether the minor version or major version of the model are increased after the transition is executed.
History Settings
Specify whether the user needs to create a comment when they execute the transition. This comment is stored in the Version history of the model (property in the chapter "Lifecycle"):
No history entry means that no entry in the version history will be created.
Optional comment by user means that the transition will be executed regardless of whether the user enters a comment or not.
Mandatory comment by user means that transition will only be executed if the user enters a comment.
Create history entry automatically means that a comment is created and stored automatically in the version history of the model. Define the content of the history entry via a support dialogue by clicking the History settings... button.
The history settings only have an impact when the Version history functionality has been turned on and configured on the Configure Mapping page. Otherwise, comments cannot be stored in the Version history of the model.
Assign Process Responsible
To automatically assign the user who executes this transition as a process responsible, select the Assign current user as process responsible check box, and then select the appropriate relation.
Example
When the default configuration of the model release workflow is in use, the current user is automatically assigned as the “Process analyst/designer” when they create a process (Initial Transition).
The setting Assign Process Responsible is only available when a transition is configured as an initial transition on the General Settings tab.
Select Referenced Transitions (e.g. for Archiving Models in the Background)
- Select referenced transitions for the model or its predecessor model. This is useful to e.g. archive the predecessor version of the model in the background.
New Version
- Select whether a new version of the model is created. This copy of the original model can e.g. be adapted and released later with an increased version number.
Validity Dates and Prolongation
Select the Set validity dates check box to set the validity period when the transition is executed:
The model is valid immediately ("Valid from" date).
Select the Override existing validity start date with current date check box to explicitly set a released model valid when this transition is executed. This allows your users to change the state of a model that is otherwise stuck in the "Released" state waiting for a scheduled "Valid from" date to arrive. By default, this option is only activated for the special transition Set valid.
Select the Set validity date to the end of the month check box to specify that the validity period always ends on the last day of a month.
By default, a model remains valid for 12 months after release ("Valid until" date). You can adapt this setting in the Duration of validity period (months) box.
The "Resubmission date" (property in the chapter Lifecycle) indicates to the responsible user(s) when the validity of the model should be rechecked. In the Resubmission date (months before validity end date) box, select how many months before the end of the validity period this date is reached.
The validity period does not affect the model release workflow as long as the prolongation scenario is not active. For example, no automatic reminders are sent before a model becomes invalid etc.
Select the Prolongate check box to prolongate the validity when the transition is executed:
- The validity period is increased by 12 months by default ("Valid until" date). You can adapt this setting in the Duration of validity period (months) box.
The last two options in this area, Prolongate and Duration of validity period (months), are only available when a transition has been configured as a Prolongate system transition on the General Settings tab.
Select whether incoming references from the predecessor model are transferred to the new version of the model.
Select whether to break outgoing relations of the target model. This function is important e.g. when archiving models. Taking the perspective of another model you can ensure that it will contain no incoming references from an archived model.
If Reset validation ToDos is activated, all ToDos are reverted to incomplete when the transition is executed.
If show success message for transition is activated, a message box will appear when all actions have been performed successfully.
Notifications
The Notifications tab is NOT available when a transition is configured as an initial transition on the General Settings tab.
The Notifications tab contains the following settings:
Send Tasks
- Define whether ADOGRC automatically sends out tasks after the transition. Tasks can be sent to notify the process responsibles and RWF roles which are responsible for executing the next transition in the release process.
Send Emails
Define whether ADOGRC automatically sends out emails after the transition (To, CC or BCC). Select one or more of the following options:
Send emails to notify the process responsibles.
noteProcess responsibles may be user based (a referenced User object) or role based (a referenced Role object). If the responsibility is defined via a Role, emails are sent to all users with that Role.
Send emails to notify the RWF roles which are responsible for executing the next transition in the release process.
Define that emails are sent ad hoc and thus allow the user in ADOGRC to select the recipients themselves.
Send emails to a predefined user list which you can prepare via a support dialogue by clicking the Add button.
Send emails to specific recipients. Enter the email addresses of the recipients in the Send to, Include as CC and Include as BCC boxes. Separate multiple entries with a semicolon.
For detailed information about how recipients influence the email notifications, see Impact of Recipients on Email Notifications for Release Workflows.
Send Emails Configuration
You can define the content of the email via a support dialogue by clicking the Email text... and Email subject... buttons. Otherwise a preconfigured email is sent.
Use plain text or HTML code with inline CSS.
You can use the following placeholders that will be replaced by actual data when the email is sent out:
%VERSIONHISTORY%: The attribute Version history.%MODELNAME%: The name of the model.%STATE%: The state of the model.%URL%: The URL for opening the model.%SENDER%: The name of the user who executed the transition.%NAME%: The first name of the email recipient.%LASTNAME%: The last name of the email recipient.%VALID_FROM%: The attribute Valid from.%VALID_UNTIL%: The attribute Valid until.%RESUBMISSION_DATE%: The attribute Resubmission date.
Before it is possible to send email notifications, the Email settings and the Base URL have to be configured correctly.
Tasks and emails can only be sent to process responsibles automatically if the process responsible functionality has been activated on the Configure Mapping page.
ADOGRC will not send out tasks or emails to members of the system role Administrator. This is to avoid spamming these users. Administrators do not have a predefined area of responsibility in the release process. They are responsible for the maintenance of the release process.
Reminder
The Reminder tab is ONLY available when a transition has been configured as a Reminder system transition on the General Settings tab.
The Reminder tab contains the following settings:
Select the Send Reminder check box to send a reminder to the responsible user(s) when the validity of the model should be rechecked:
In the Reference date box, select whether the reminder shall be sent "On Resubmission", before the "Valid until" date, after the "Valid until" date or after the "State change".
In the Months/Days area, choose how many Months or Days before/after the Reference date the reminder is sent. For example, if "After State change" is selected as the Reference date and 7 days as the interval, the reminder will be sent 7 days after the model has changed state. This option is not available when the reminder is sent "On Resubmission".
From the Interval list, select the interval in which reminders are sent.
In the Occurrence box, choose how many reminders are sent.
Voting
The Voting tab is ONLY available when a transition has been configured as a Vote system transition on the General Settings tab.
The Voting tab contains the following settings:
Select the Active check box to initiate a voting process on the model before the transition is executed. All other options in the Voting area are inactive unless you select this check box.
From the Responsible which represents voters list, select who the responsible persons are that may vote. All Users or Roles which are referenced in the properties of the model in the selected relation can cast their votes.
infoOnly one role owner can vote per Role.
Click the Define voting question button to define which text is displayed when voters are asked to vote on a model. Enter a text for every language ADOGRC supports. Otherwise ADOGRC displays a preconfigured text.
To specify that users need to create a comment when they vote with Yes or No, select the Active mandatory comment if user voted with check box, and then select the appropriate check boxes. This comment is stored in the version history of the model (property in the chapter "Lifecycle").
In the Define follow up transitions area, select the transitions after the vote.
From the Transition in case of negative voting result list, select the transition if the vote fails.
From the Transition in case of positive voting result list, select the transition if the vote succeeds.
For both of these options, select the Start automatically check box so that the follow up transition is automatically executed after the vote.
noteIf you deactivate Start automatically, the follow up transition has to be executed manually. In this case, both follow up transitions (...negative voting result and ...positive voting result) will be available.
In the Transition available while voting is in progress area, select which transitions may be executed to abort the voting process. These transitions must have the same source state as the voting transition.
In the Voting strategy area, you can define when the voting process ends:
All votes are received means that all voters need to vote.
Threshold is reached means that a minimum percentage of positive votes must be received. The vote also ends when too many voters have voted negative and the vote can no longer be successful. You can specify the minimum percentage in the Threshold (minimum percentage of positive votes) (%) box below.
In the Threshold (minimum percentage of positive votes) (%) box, specify the minimum percentage of positive votes needed to make the vote successful. If the option Threshold is reached is selected, the vote will end as soon as the threshold is passed.
Configure Voting
Voting processes may be used in sophisticated release workflow scenarios. Typically, a group of people decide whether a model will be released. When the default configuration of the model release workflow is in use, this feature is disabled.
In ADOGRC, a voting process is represented by a transition. After the vote ends, different follow up transitions may be executed depending on whether the voting result was positive or negative (e.g. Reject or Release). You can configure multiple voting processes within the model release workflow.
Only one voting process may be configured per target state.
Configuration Variants
Depending on the release workflow configuration in use, different steps are necessary to configure voting. The following variants are possible:
Activate Voting for Release
Are you using the default configuration of the model release workflow? In this case, you can activate a preconfigured voting process on models before they are released. In order to do so:
Open the Configure Transitions page.
Open the transition Vote for release for editing.
On the Voting tab, select the Active check box, and then click Save.
Click Save.
The voting process is activated and ready for use. All Users or Roles which are referenced in the properties of the model as Process managers can cast their votes.
Only one role owner can vote per Role.
Once all votes are received, voting ends. The Process owner can then execute the follow up transition manually (either Reject or Release based on the result).
Configure Voting for any Particular Transition
The following steps are necessary to configure voting for any particular transition:
Map model relation that will represent voters
Create transition - general settings
Create transition - conditions
Create transition - voting
Map Relation that Will Represent Voters
In order to map the relation that will represent voters:
Open the Configure Mapping page.
In the Process responsible functionality area, select the Active check box.
Make sure that the relation which represents voters is defined here. You can either use the Process owner, Process manager or Process analyst/designer relation or define an additional relation.
Create Transition — General Settings
In order to create a transition representing the voting process and to configure general settings:
Open the Configure Transitions page.
Click the Add new transition button.
In the Language independent name box, type a name for the transition. This language-independent name uniquely identifies the transition.
In the language specific text boxes, type a name for every language ADOGRC supports. These names are visible on the user interface.
Select the Create menu item check box.
In the Configure states area, change both the source state and the target state to the state in which the voting process is started.
Example
You want to configure a voting process on released models before they are archived. Change the source state and target state to Released.
In the System transition area, select Vote from the list.
Create Transition — Conditions
In order to configure conditions for the voting process:
Switch to the Conditions tab.
In the RWF roles which are allowed to execute this transition area, define the system roles which are allowed to execute this transition. Voters must have at least one of these system roles.
In the Model type selection area, define for which model types this transition is enabled.
In the Process responsibles who are allowed to execute the transition area, select the Active check box, and then select the relation which represents voters.
Create Transition — Voting
In order to configure actions for the voting process:
Switch to the Voting tab.
Select the Active check box.
From the Responsible which represents voters list, select the relation which represents voters. All Users or Roles which are referenced in the properties of the model in the selected relation can cast their votes.
infoOnly one role owner can vote per Role.
From the Transition in case of negative voting result list, select which transition may be executed if the vote fails.
Example
You want to configure a voting process on released models before they are archived. Change the Transition in case of negative voting result to No transition selected (= model remains in the state Released).
From the Transition in case of positive voting result list, select which transition may be executed if the vote succeeds, and then click OK
Example
You want to configure a voting process on released models before they are archived. Change the Transition in case of positive voting result to Archive.
Click Save, and then click Save.
The voting process is activated and ready for use.
Other settings are optional (you can use the default configuration). For example, you may specify that the follow up transition is started automatically when the vote ends etc.
Configure Assignment of Specific Methodical Reviewers
By default, all users with the system role "Reviewer (methodical)" may perform methodical reviews on all models. The Methodical Reviewer attribute enables a better reviewer responsibility assignment. It allows assigning specific methodical reviewers to models if the model release workflow configuration is adapted accordingly.
The following steps are necessary to configure assignment of specific methodical reviewers:
Adapt Transition "Submit to Methodical Review"
Adapt Transition "Submit to Business Review"
Final steps
The procedure described here is only valid if the default configuration of the model release workflow is in use. If you are using another configuration, the required steps depend on the design of the release workflow transitions.
Adapt Transition "Submit to Methodical Review"
In order to adapt the transition "Submit to methodical review":
Open the Configure Transitions page.
Open the transition Submit to methodical review for editing.
Switch to the Checks tab.
In the Process responsible area, select the Methodical reviewer check box , and then click Both.
Switch to the Notifications tab.
In the Send tasks area, do the following:
Select the Send tasks to process responsible check box, and then select the Methodical reviewer check box.
Clear the Send tasks to RWF roles check box.
In the Send emails area, do the following:
Select the Send emails to process responsible check box, and then select the Methodical reviewer check box.
Clear the Send emails to RWF roles check box.
Click Save.
Adapt Transition "Submit to Business Review"
In order to adapt the transition "Submit to business review":
Still on the Configure Transitions page, open the transition Submit to business review for editing.
Switch to the Conditions tab.
In the Process responsibles who are allowed to execute the transition area, select the Active check box , and then select the Methodical reviewer check box.
Click Save, and then click Save.
Final Steps
Perform the following final steps:
- Restart the ADOGRC application server.
The assignment of specific methodical reviewers is activated and ready for use.
Configure Prolongation
When the prolongation mechanism is in use, a modeller can set a date from which a model will be valid after it is released. By default a model is valid for one year after it is released. Before the model becomes invalid, a reminder is sent to the responsible user(s). The reviewer can then prolongate the model. If the reviewer requests changes, the modeller may create a new draft version in order to adapt the model. Alternatively, the model may be archived.
When the prolongation mechanism is activated, each night at 1:00 AM local time validity of all versioned models is automatically checked on the ADOGRC application server. This validity check has two effects:
When the "Valid from" date has been reached, the state of versioned models changes to "Valid".
When the "Valid until" date has been reached, the state of versioned models changes to "Invalid".
Configuration Variants
Depending on the release workflow configuration in use, different steps are necessary to use the prolongation mechanism. The following variants are possible:
Default Configuration of the Model Release Workflow
In order to use the prolongation mechanism when the default configuration of the model release workflow is in use:
Import the extended release workflow configuration that includes the prolongation mechanism configuration (Import component settings). The respective file
ADONIS 17.2 - RWF Standard config (incl. prolongation mechanism).axscan be found in the folder “04 Sample Data\Component Settings“ in the installation package. Overwrite the existing configuration with the content of the import file.Restart the ADOGRC application server.
The prolongation mechanism is activated and ready for use.
Adapted Default Configuration of the Model Release Workflow
Are you using a default configuration which has been adapted (additional states or system roles etc.)? The following steps are necessary in order to use the prolongation mechanism:
Activate prolongation mechanism
Adapt source states of existing transitions
Adapt transition "Release"
Adapt transition "Set valid"
Final steps
Activate Prolongation Mechanism
In order to activate the prolongation mechanism:
Open the Configure Mapping page.
In the Prolongation Configuration area, select the Active check box.
The other settings in this area are optional (you can use the default configuration).
Adapt Source States of Existing Transitions
In order to adapt the source states of the existing transitions:
Open the Configure Transitions page, and then open the transition New draft version for editing.
In the General settings tab, remove the source state Released, and then click Save.
Repeat steps 1 - 2 for the transitions Archive and Archive model (system).
Adapt Transition "Release"
In order to adapt the transition "Release":
Still on the Configure Transitions page, open the transition Release for editing.
Switch to the Actions tab.
In the Transition of model list, change the transition from No transition selected to set valid at validity start point. The target state of the model will automatically change from Released to Valid when the "Valid from" date is reached.
In the Transition of predecessor model list, change the transition from Archive model (system) to No transition selected.
Clear the Transfer references from predecessor model check box, and then click Save.
Adapt Transition "Set Valid"
In order to adapt the transition "Set valid":
Still on the Configure Transitions page, open the transition Set valid for editing.
In the General settings tab, select the Create menu item check box.
Click Save, and then click Save.
Final Steps
Perform the following final steps:
- Restart the ADOGRC application server.
The prolongation mechanism is activated and ready for use.
Specific Configuration of the Model Release Workflow
If you are using a specific configuration, the required steps to activate the prolongation mechanism depend on the design of the release workflow transitions.
A complete description of all configuration possibilities goes beyond the scope of this manual. Please contact your ADOGRC consultant. They will help you get a new release workflow configuration that includes the prolongation mechanism.
Configure User Rights for the Model Release Workflow
In this section rights settings for two typical scenarios when using the model release workflow are summarised.
Global Rights Settings: One set of permissions is applied across the organisation
Business Unit-Based Rights Settings: Permissions are different depending on the business unit or department
All descriptions in this section refer to the default configuration of the model release workflow. If you are using a different configuration, adjust the rights settings analogously to the settings described here.
Global Rights Settings
One set of permissions is applied across the organisation (and its business units). This scenario often applies to smaller and/or centrally managed organisations.
Scenario Description
- Only Modellers can create new models or new versions of released models.
This only applies to model types configured for use in the model release workflow. The use of other model types is not restricted.
Modellers have write access to models in the state Draft across all business units.
Models which are not in the state Draft are read-only for all users with a release workflow role.
Reviewers can review submitted models across all business units.
Readers have read access to models across all business units. In the Organisation Portal, Readers only have access to released models.
Procedure for Setting the Necessary Rights
The individual business units are represented by model groups.
Add users to the appropriate system roles depending on their task in the release process. Readers do not a have a release workflow role.
Add users to the following user groups:
Assign Modellers to a user group that provides write access to all model groups that contain models in the state Draft. This is necessary for the Modellers to create new working versions.
Assign Readers to a user group that only provides read access to all model groups.
Business Unit-Based Rights Settings
Different sets of permissions are assigned depending on the user's area of responsibility and business unit within the organisation. This scenario applies to larger and/or decentrally managed organisations.
Scenario Description
- Only Modellers can create new models or new versions of released models.
This applies to the subset of model types configured for use in the model release workflow. The use of other model types is not restricted.
- Modellers have write access to models in the state Draft in their business unit only. They do not have write access to models in other business units.
Example
Modeller A can create models in "BU1". He only has read access to models in "BU2" and no access to models in "BU3".
Models which are not in the state Draft are read-only for all users.
Reviewers can review submitted models across all business units.
Readers have read access to models across all business units. In the Organisation Portal, Readers only have access to released models.
Some Readers (or groups of readers) may not be allowed to see all released models, but only of certain business units.
Procedure for Setting the Necessary Rights
The individual business units are represented by model groups.
Add users to the appropriate system roles depending on their task in the release process. Readers do not a have a release workflow role.
Add users to the following user groups:
Assign Modellers to a user group that provides write access to all model groups that contain models of their business unit in the state Draft. This is necessary for the Modellers to create new working versions.
Assign Readers to a user group that only provides read access to all model groups. If necessary, restrict the rights further and do not grant access to specific model groups.
ADOGRC Release Workflow
ADOGRC provides release workflows for several ADOGRC object types. To enable users to execute their tasks within the release workflows, it is necessary to assign these users the workflow roles which match their role in their company's organisation.
ADOGRC Workflow Roles
The workflow roles are used to give users access to the ADOGRC workflow functionality, such as performing transitions and creating new versions of objects. These system roles are automatically provided by the ADOGRC Standard Application library. There are two roles for each ADOGRC workflow:
Administrator: The Administrator role enables a user to intervene in operational workflows, such as declining/rejecting an object out of its current position in the workflow. This can become necessary in some cases where an object would otherwise be "stuck" in a certain state due to external factors (e.g. if the currently responsible employee left the company). This role is not meant to be used for regular workflow tasks.
User: The User role is the standard role assigned to users executing object release workflow transitions.
Additional Workflow Roles
Some ADOGRC workflows have an Additional Workflow Role with supporting features in the user interface, which is required and must be assigned together with the Workflow Roles. These roles are only available for the following object types: Control, Control Execution, Control Testing, Risk, Risk Assessment and Initiative.
When a user is assigned a Workflow Role (e.g. ADOGRC - Release Workflow: Control execution / User), they have to be assigned the corresponding Additional Workflow Role (e.g. GRC-Release Workflow: Control Execution).
Special System Roles
ADOGRC ships with special system roles which depend on the type of tasks a user executes:
GRC-Contributor: This is a system role which provides common functionality for all users contributing to a release workflow. It allows users to create, edit or otherwise interact with objects during workflows and is therefore required alongside the ADOGRC Workflow Roles.
GRC-Reader: This role is intended for users who only need access to information about ADOGRC objects and do not participate actively in a release workflow. It offers access to dashboards and tabular views but allows only limited access: only objects in a released state will be visible and the user will not be able to create and edit objects or execute tasks in the release workflow.
This role includes access to additional dashboards in the Read & Explore scenario of ADONIS. It is therefore mandatory to assign this scenario to users with the GRC-Reader role. If the user does not have access to the Read & Explore scenario, the configuration is invalid and the user will not be able to log in.
GRC Scenario Manager: This role is intended for users who organize ADOGRC objects into specific GRC scenarios and domains. It allows the user to quickly assign a large number of objects in a single bulk action from the context menu. Users without this role can assign a GRC scenario only individually, when they create or edit an object.
ADOGRC Scenario Role
The ADOGRC - GRC Scenario role is a special named-use system role which allows access to the ADOGRC start page - the central hub for all GRC tasks. This page offers dashboards and tables with current, upcoming and overdue tasks for users and allows them to directly access all objects required for their tasks. To be able to use the ADOGRC Scenario, users need to be assigned the workflow roles of at least one release workflow as well as the GRC-Contributor role.
Typical Role Assignments
The following table gives a few examples to illustrate some typical role assignments for users participating in the ADOGRC workflows and activities. Depending on the role and position of a user in their company's organisation, these assignments need to be adapted according to the tasks a user will have to execute.
| Workflow | Role Assignment for User |
|---|---|
| Risk Master Data |
|
| Risk Assessment |
|
| Control Master Data |
|
| Control Execution |
|
| Control Testing |
|
| Initiative |
|
| Control Objective Master Data |
|
| Control Objective Assessment |
|
| Processing Activity Master Data |
|
| GRC-Reader |
|
ADOGRC Release Workflow Consistency Checks
When initiating a release workflow transition, ADOGRC executes a number of consistency checks to ensure that the object is in a valid state for this transition. In case it finds an error during these checks, the transition is cancelled and an error message is shown along with a hint on how to rectify the issue. There are also checks which do not block a transition but issue a warning that best practices have not been met. This can happen if some attributes have not been filled which are usually considered necessary or alert the user to double check possible inconsistencies.
A list of consistency checks can be found in the Appendix Validation Checks Overview in the section ADOGRC Consistency Checks.
Organisation Portal
Starting with ADONIS 15.0 + ADOGRC 12.0, the Organisation Portal is no longer available to new customers. Existing customers with licences that include the Organisation Portal may continue to use it.
The Organisation Portal allows employees of your organisation easy and intuitive access to the models in the ADOGRC database. Personalized dashboards and other complex functions are not included in the Organisation Portal. Access to the Organisation Portal does not require a user account.
The Organisation Portal is read-only. Users have no write access to repository content (including all models and objects and their relations).
Set Up Access to the Organisation Portal
In order to set up access to the Organisation Portal you need to prepare at least one user account with the appropriate system role. The following steps are necessary to set up the default configuration:
Create the following top level user group:
- Reader
Edit the access rights of the user group "Reader" for the following groups at the top level just below the root groups:
Read access to the model group "Models"
Read access to the object group "Objects"
Create the following user account and add it to the newly created user group:
- User name: Reader, and a password of your choice. Activate Trusted Login and assign the current standard repository to the user.
Assign the following preconfigured system role to the newly created user group:
- Organisation Portal
By default, the system role 'Organisation Portal' has access to the following modules only:
- BPMS Organisation Portal
The above settings represent the minimum configuration. You can assign additional modules to the system role "Organisation Portal". Bear in mind though that if a user has access to more functionality via additional modules, the complexity of the Organisation Portal as a whole increases.
The system role "Organisation Portal" must not be assigned in combination with other system roles.
The ADOGRC application server has to be restarted if these settings are changed. Otherwise the changes will not become effective.
Configure Organisation Portal
To configure the Organisation Portal:
- Go to Settings > Organisation Portal > General.
The Organisation Portal configuration wizard has 2 pages:
These pages are discussed in more detail in the following sections.
The ADOGRC application server has to be restarted if these settings are changed. Otherwise the changes will not become effective.
General Settings
The first page of the Organisation Portal configuration wizard allows you to grant or deny anonymous access to the Organisation Portal and select which model states should be visible.
Access Configuration
The following settings are available:
- Allow anonymous access: Choose whether to enable anonymous access to the Organisation Portal, allowing users entry without having to provide credentials. Deactivating this option is useful in case of publicly accessible deployments when allowing access to the Organisation Portal without authentication is not desirable.
Deactivating this option has the following effects:
Only authenticated users with the system role 'Organisation Portal' may log in to the Organisation Portal.
The link to access the Organisation Portal on the ADOGRC login page is not displayed.
Access to the Organisation Portal via user-specific URLs is disabled.
The menu entry Organisation Portal from the dropdown menu for scenario selection in ADOGRC is disabled.
The Organisation Portal configuration options Access via the link on the web client login page, Default user for anonymous access and Activate user-specific URL become inactive.
Access via the link on the web client login page: Select whether a link is displayed on the ADOGRC login page that allows users to enter the Organisation Portal. The Standard user (see below) is utilized in this case.
Default user for anonymous access: Select which user account is utilized when users enter the Organisation Portal via the link on the ADOGRC login page.
State Filter Configuration
The model state filter lets you control the visibility of models in the Organisation Portal. You can select which model states should be visible and for which model types the filter should be applied.
Choose model types to which the state filter should be applied: Select the model types for which the filter should be applied. Model types which are not selected will be visible regardless of state.
Select states to be shown: Select the model states which should be visible if the model state filter is applied.
Configure Start Model
The second page of the Organisation Portal configuration wizard allows you to configure user-specific and repository-specific entry points to the Organisation Portal, as well as establish a start model for each of these entry points.
Users
This tab lists all user accounts with the system role "Organisation Portal".
You can configure different users (different settings for the Organisation Portal and different user rights). This allows you to provide multiple entry points to the Organisation Portal and to restrict access to the available repository content for employees of your organisation.
Trusted Login is a prerequisite for user accounts which are used to access the Organisation Portal anonymously.
Name: The first column contains the name of the user account.
User-specific URL: This column contains the URL that allows users to enter the Organisation Portal anonymously, without having to provide credentials. Access rights to the models in the database are based on the user account that is used and on the settings for the Organisation Portal.
The URL is composed of the Base URL and the suffix ?reader=<user account>, e.g. http://server:8000/ADONIS17_2?reader=Reader2.
Click
Copy to copy the URL to the clipboard, and then paste the URL where you need it.
Selected repository: If a start model has been selected for this user-specific URL, the repository that contains the start model will be displayed here.
Start model: Here you can specify a start model that will appear on the Organisation Portal start page. Click Configure start model, and then choose a repository and the start model you want. If a start model has been selected for this user-specific URL already, it will be displayed here.
There is a special fallback handling when you import Organisation Portal component settings from ADOGRC 14.1 or lower. The start model for the Default user for anonymous access (see above) will also be displayed on the "Read & Explore" scenario start page as long as no specific "Read & Explore" start model has been defined (see Read & Explore Scenario).
Activate user-specific URL: Select whether anonymous access to the Organisation Portal with this user is possible. This option is useful if you want to temporarily disable an entry point to the Organisation Portal instead of permanently removing it.
When you deactivate this option, the user-specific URL to access the Organisation Portal with this user is disabled. Additionally, in case of the Standard User (see below), the link to access the Organisation Portal on the ADOGRC login page is not displayed and the menu entry Organisation Portal from the dropdown menu for scenario selection in ADOGRC is disabled.
Repositories
This tab lists all repositories. You can define a fallback configuration for each of these repositories. These fallback configurations are used when the option Activate repository fallback is activated.
- Activate repository fallback: Select this check box to enable a fallback mechanism for authenticated users with the system role 'Organisation Portal' that do NOT have a user-specific Organisation Portal configuration. When such users log on to ADOGRC, a fallback configuration is used. This is useful in case of deployments where large numbers of users with the system role 'Organisation Portal' are automatically created but configuring them individually is not feasible.
Start model: Here you can specify a start model that will appear on the Organisation Portal start page. Click Configure start model, and then choose the start model you want. If a start model has been selected for this fallback configuration already, it will be displayed here.
Active: Select whether access to the Organisation Portal with this fallback configuration is possible. This option is useful if you want to temporarily disable an entry point to the Organisation Portal instead of permanently removing it.
Absence of Start Model and Impact of Model Release Workflow
Explore the implications of not configuring a start model for the Organisation Portal and understand the influence of the model release workflow on start models. Read on for the details.
No Start Model Configured
When no start model has been configured for the Organisation Portal, the following applies:
- In the Organisation Portal, the appearance of the start page changes. The "Home" section with the start model is not displayed. Instead, the "Processes" section will appear as the start page.
Start Model and Model Release Workflow
When the model release workflow is in use, the start model for the Organisation Portal is automatically updated to use the latest released version of a model.
Example
You have defined a Process Landscape (version number "1.00") as your start model. A new version of this Process Landscape is released. The new model (version number "2.00") will be displayed as a start model instead of the archived predecessor version.
Configure IP Restrictions for the Organisation Portal
If you want to limit which IPs can access the Organisation Portal, you need to adapt the Security settings in the ADOGRC Administration:
Go to Authentication > More options, and then click Security Settings.
Switch to the Org Portal IP Restrictions tab.
Adapt the following setting:
- Org Portal IP Restrictions: This setting is optional. You can restrict the IP addresses that are allowed to access the Organisation Portal (see Configure IP Restrictions for more information).
Process Drafter
The settings in this area allow you to prepare your instance to be used with the Process Drafter. Please refer to the Process Drafter Guide for details.
The Process Drafter is only available in the ADONIS Enterprise Edition.
Process Analysis & Optimisation
Here you can define default values for simulation parameters and general settings for process analysis (process simulation and process stepper). For details on how to configure this, please refer to the relevant section in the ADONIS Administration Help
Process Mining Essentials
The settings in this area allow you to prepare your instance to be used with Process Mining Essentials (PME) of ADONIS. Please refer to the Process Mining Essentials (PME) Guide for details.
PME is a licensable add-on for the ADOGRC Enterprise Edition.
Property Filter
Property filters control the visibility of properties (= attributes and relations) in the following areas:
Tabular Editor
Properties pane
Reports
Model Comparison
You can define different property filters for different system roles and scenarios.
Open Property Filter Settings
To open the property filter settings:
- Go to Settings > Property Filter > General.
Add and Configure Property Filter
To add a new property filter:
Click the Add filter button.
In the Language independent name box, type a name for the property filter. This language-independent name uniquely identifies the filter.
In the Display name area, type a name for every language ADOGRC supports. These names are visible on the user interface.
In the Order area, select the order of the entries when a user selects a property filter in ADOGRC.
In the System role assignment area, select the system roles to which you want to assign this filter.
In the Scenario assignment area, select the scenarios to which you want to assign this filter.
On the Model types, Classes and Relation classes tabs, select the properties which should be visible when a property filter is active. You can also select entire chapters (into which the properties are organised) or even all properties at once.
Click Add filter, and then click Save. The new property filter is added and the component settings are saved.
Optionally you can also:
- Select an existing configuration as a template for your new property filter. On the General
page, in the Property filters area, find the filter you want to use. To the right of the
property filter, click
More, and then click Copy.
You can combine system role assignments and scenario assignments. A property filter is only visible if all conditions are met (logical AND operator).
Edit or Delete Property Filter
You can edit property filters to fine-tune them, and delete property filters you no longer need:
- On the General page, in the Property filters area, find the filter you want. To the right of
the property filter, click
More, and then click Edit filter or Delete.
Settings per Scenario
In this section, you can configure which property filter should be enabled by default in ADOGRC. You have the option to set the default filter for all scenarios ("Global") and to define different default filters for specific scenarios as needed.
Global
On the "Global" tab, you can define the default filter for all scenarios. The following settings are available:
Default filter: Select which property filter should be enabled by default. If a user does not have access to the selected filter, the first filter on the list is activated, then the second filter and so on.
Enable 'Show All' Filter: Select this option box to make the Show all filter available to all users. When the Show all filter is active, all properties are visible.
Enable 'Hide empty attributes' filter in Properties in 'read mode': Select this option to make the Hide Empty Attributes filter available to all users. When the Hide Empty Attributes filter is active, no empty properties are visible in read mode.
Scenario-Specific Filter Settings
On the tabs for individual scenarios such as "Read & Explore" or "Design & Document", you can define scenario-specific filter settings. The following settings are available:
Use default settings: Clear this option to enable scenario-specific filter settings.
Default filter: Select which property filter should be enabled by default in this scenario.
When a filter is defined as default for a scenario, switching to this scenario will always set this default filter, no matter which filter was active before.
- Enable 'Show All' Filter: Select this option to make the Show all filter available to all users in this scenario.
Read & Explore Scenario
The Read & Explore scenario is a read-only scenario in ADOGRC where users can view processes and working instructions. You can configure various settings for this scenario. For example, you can choose whether the widgets and dashboards display data based on Roles or Organisational Units. You can also select the default model editor and choose which start model should appear on the Read & Explore scenario start page.
Open Read & Explore Scenario Settings
To open the Read & Explore scenario settings:
- Go to Settings > Read & Explore Scenario > General.
General Settings
The following settings are available:
My Processes Based on: Select what data to display in the widgets and dashboards of the "Read & Explore" scenario. The processes categorised as "My processes" can be derived either from the assignment of Users to Roles or to Organisational Units.
Activate Assignment of Roles by Readers: This option is only available if My Processes based on is set to Roles. in ADOGRC, in the "Read & Explore" scenario, at the top of the My BPM dashboard, the Roles which are associated with the field of responsibility of the current user are displayed ("My Roles"). Select the check box to allow users to add Roles from other areas of responsibility. The selection of Roles determines what data will be loaded in the widgets of the “Read & Explore” scenario.
noteThe Roles which are relevant for the "Read & Explore" scenario are Role objects referenced in the properties of the User object. They should not be confused with system roles.
Set Textual View as Default Editor: Select this option to make the textual view the default editor in the "Read & Explore" scenario. All model types with a textual view configuration will be opened in the textual view by default. When you clear this option, the graphical editor will be the default editor for all model types.
Activate State Filter (Show only Released Models and Objects): Select this check box to only show models and objects in the state "Released" in the "Read & Explore" scenario. Model and object types without a state set by a release workflow are not affected.
Allow Users to Configure Start Model: Select this check box so that users can set their own start models for the "Read & Explore" start page. For this option to work, Enable start model (see below) must also be activated for the repository.
Select Start Model per Repository
Here you can specify a start model that will appear on the "Read & Explore" scenario start page. You can define a configuration for each repository.
The following settings are available:
+ Select Repository: Choose the repository for which a start model should be set up.
Enable start model: Select whether a start model will be displayed.
+ Select Model: If Enable start model is activated, you can select the start model here.
Recommender Service
The Recommender Service is designed to enhance the ADONIS experience by suggesting models that may complement each other. This functionality is accessible within the Read & Explore scenario, specifically in the graphical editor, making it easier for users to discover relevant models and get inspired by the work of their colleagues in the organisation. For details on how to configure this, please refer to the relevant section in the ADONIS Administration Help
This service is disabled by default and must be manually enabled by an authorised administrator following the instructions provided below. Please note that the required collection of anonymous data will begin only after the service is activated, so there may be a delay before it functions properly.
The service uses AWS Cloud (eu-central-1), regardless of your chosen deployment option for ADOGRC (SaaS or on-premise).
Open Recommender Service Settings
To open the Recommender Service settings:
- Go to Settings > Recommender Service > General.
Configure Recommender Service
The following settings are available:
- Enable recommender service per repository: Select the repositories for which the Recommender Service should be enabled.
How Long Until Model Recommendations Are Ready?
Once enabled, the Recommender Service must undergo training before it can provide model recommendations.
Training data is uploaded to the service on the 1st and 15th of each month at 06:30 local time of the web server. Once the first training session is completed, you can expect recommendations to be displayed promptly.
Example
If you enable the service on the 8th of the month, the training data will only be uploaded on the 15th. Therefore, no recommendations will be displayed until after the first training session on the 15th.
Privacy and Data Usage Statement for ADOGRC Recommender Service
The Recommender Service for ADOGRC is a microservice deployed within the AWS Cloud (eu-central-1) and is designed to help users navigate through the models within their own ADOGRC repository. It does so by learning from previous user behaviour and recommending models to visit next, based on previously visited models.
After activating the service, ADOGRC collects anonymous data about which models in your repository have been opened and in what order. Such data is kept until newer data is uploaded to the service (typically within two weeks). To provide the service, the following strictly anonymous data is used:
UUID of the ADOGRC repository
in what order specific models were opened
UUID of opened models
information on which models were opened in a user session
This data is not linked to specific users and and is solely used within your repository. Users in your repository will not receive recommendations based on the behaviour of users in other repositories or vice versa.
Furthermore, during the use of the Recommender Service, the following incoming data is logged:
UUID of the ADOGRC repository for which the recommendation is generated
UUIDs of the previously opened models (up to 5)
order of the previously opened models
The BOC Group reserves the right to discontinue or pause the Recommender Service at any time.
General Terms for Microservices
Please note: The use of microservices is additionally governed by Section 9 ("Microservices") of our Terms of Use – Subscription Services. By using microservice-based features, you agree to the conditions outlined therein.
Allow the Recommender Service URLs on Your Firewall
On-premise customers who want to use the Recommender Service must ensure that certain URLs are allowed through their firewall. You'll need to identify the configured URLs for the Recommender Service and add these, along with one additional URL, to your allowlist.
SaaS customers can skip this step, as the necessary firewall configuration is handled by our Cloud Operations team.
Prerequisites
Before you proceed, you need to assign two modules to your user in the ADOGRC Administration. These modules are required to access the connection configuration:
Go to Settings > System settings > Modules.
Assign the following modules to one of your system roles:
Generic Connector
Module: Connect Admin
Look up URLs
To find the configured URLs for the Recommender Service in the ADOGRC Administration:
Go to Settings > More options, and then click Connect Center.
In the left pane, under Connectors, select the AWS Recommender configuration, and then click Open configuration dialog
.
Open the Technical Settings tab, copy the URL from the URL box and save it for later use. Then, close the configuration.
Repeat steps 2 - 3 for the AWS Cognito configuration.
Add URLs to Firewall Allowlist
Add the following URLs to your firewall's allowlist:
https://s3.eu-central-1.amazonaws.comThe AWS Recommender URL (as identified above)
The AWS Cognito URL (as identified above)
SCIM Services
ADOGRC supports user lifecycle management (ULM) via SCIM. This standard REST protocol lets external systems automatically handle user and user group setup, updates, and removal in ADOGRC, following the SCIM 2.0 standard.
To use SCIM services, your license must include the REST API component.
Activate Access to the SCIM Services
Instructions on how to activate access to the SCIM services are covered here in the Administration Help.
You must first perform the following steps:
Create Technical User (required for OAuth 2.0 using the Client Credentials Flow and token based authentication only)
Then you can configure the authentication method you want to use to communicate with the SCIM services:
These steps are explained in the following sections.
Use the SCIM Services
For information on how to use the SCIM services, please refer to the BOC Developer Portal, especially:
More
Find extra resources to help you understand the SCIM implementation in ADOGRC:
Create Technical User
Do you want to use OAuth 2.0 authentication using the Client Credentials Flow for authenticating requests to the SCIM API, or token based authentication? If yes, you need to create a technical user now.
A technical user is NOT required for the other authentication methods used with the SCIM API, so you can skip this step if you're using one of those methods.
To create the technical user in the ADOGRC Administration:
Go to the Users page and click New User.
Begin by filling out the account details on the General tab:
Enter a name for the technical user, e.g. "Technical_SCIMServices".
Enter and confirm a password of your choice.
Next, go to the Groups and Roles tab:
- Under User groups, click Select user groups and assign the user to the Default group.
Next, go to the Repository tab:
- Click Select repository and assign all repositories to which users may be assigned by the SCIM API.
Click Create to complete the user creation process.
Once user creation is complete, you can enable trusted login for the user:
Hover over the user, click
More, and then select Edit.
On the General tab, under Trusted login, select Enabled.
Edit System Settings
Now you have to define a few technical settings controlling the base functionality of ADOGRC in the ADOGRC Administration. To edit the System settings:
Go to Settings > System settings > System.
The Base URL field must contain the URL where ADOGRC can be reached from other machines.
Do you want to use OAuth 2.0 authentication using the Client Credentials Flow or token based authentication? If yes, click Select users and select the technical user you created, e.g. "Technical_SCIMServices" (see Create Technical User).
Click Save.
Activate Access to the SCIM Services
To activate SCIM services, proceed as follows:
Go to Settings > SCIM Services > General.
Select Enable SCIM Services globally to activate the feature. All other settings in this area are inactive unless you select this option.
You can now configure the authentication method you want to use to communicate with the SCIM services.
Configure Basic Authentication
You need to enable basic authentication in the SCIM Services settings (see Configure Settings for Basic Authentication) and in the Security settings (see Enable Basic Authentication for ADOGRC).
Basic authentication is the simplest authentication method and may be suitable for test environments. Ensure SSL/TLS is enabled as described in the ADONIS Installation Manual for secure communication.
Configure Settings for Basic Authentication
To enable Basic Authentication for SCIM services:
Go to Settings > SCIM Services > General > Basic Auth.
Select Enable basic authentication.
Enable Basic Authentication for ADOGRC
For security reasons, basic authentication is turned off by default in ADOGRC. If you want to use the SCIM Services with basic authentication, you need to adapt the Security settings in the ADOGRC Administration:
Go to Authentication > More options, and then click Security Settings.
Switch to the SCIM tab.
Adapt the following settings:
- Basicauth IP Restrictions: Specify the IP addresses that shall be allowed to send requests with basic authentication to the SCIM API (see Configure IP Restrictions for more information).
- Basicauth Roles: This setting is optional. Select system roles that a user must have at least one of in order to use the SCIM API with basic authentication. If no system role is selected, all system roles will allow access to the API.
No restart is required when modifying these settings.
Configure OAuth 2.0 Authentication
You need to enable OAuth 2.0 authentication in the SCIM Services settings (see Configure Settings for OAuth 2.0) and in the OAuth 2.0 settings (see Enable OAuth 2.0 for ADOGRC).
OAuth 2.0 is a recommended method for secure automated provisioning in enterprise environments. Ensure the configured IdP supports SCIM with OAuth.
Configure Settings for OAuth 2.0
To enable OAuth 2.0 authentication for SCIM services:
Go to Settings > SCIM Services > General > OAuth 2.0.
Select Enable OAuth 2.0.
Click Add scopes to configure access scopes, if needed (see below).
Scopes (Client Credentials Flow)
OAuth 2.0 offers multiple flows. ADOGRC supports the Authorization Code Flow and the Client Credentials Flow.
Do you want to use the Client Credentials Flow? If yes, you need to define at least one scope:
Add Scope: To add a new scope, click Add scopes.
Edit or Delete Scope: To the right of the scope, click
More, and then click Edit or Delete.
A scope consists of the following parts:
name
IP constraints
technical user
SCIM services support multiple scopes. At least one scope is required.
When would you want to use multiple scopes? You can execute requests with access rights of different technical users or from different IP ranges. During execution, you can choose which of the predefined scopes should be used.
Let's take a detailed look at the settings:
Name: This parameter represents the name of the scope. Enter a descriptive name, e.g. "SCIM_FULL".
IP constraints: This parameter is optional. You can restrict the IP addresses that shall be able to access a scope by passing an IP constraint pattern. Here's how the configuration works:
An IP constraint consists of a comma separated list of rules.
A rule consists of a keyword ('allow' or 'deny') followed by a white space, and an IP address or address with wild card * (e.g. 192.168.*). The keyword "all" can be used to match all addresses.
If rules are present, but no match is made, the default setting is "deny".
If no rules are present, the default setting is "allow".
The first matching rule decides. E.g. when you formulate a constraint like "allow 192.*, deny 192.168.0.1", the 'deny' rule would have no effect, as that address matches the 'allow' rule already.
Example
Deny all IP addresses starting with 192., deny the IP address 193.168.0.1, allow all other IP addresses:
deny 192.*,deny 193.168.0.1,allow all
Allow all IP addresses starting with 178. except 178.6.6.6, deny all other IP addresses:
deny 178.6.6.6,allow 178.*
- Technical user: Select the technical user you created, e.g. "Technical_SCIMServices" (see Create Technical User).
Enable OAuth 2.0 for ADOGRC
For security reasons, OAuth 2.0 authentication is turned off by default in ADOGRC. If you want to use SCIM services with OAuth 2.0, you need to enable OAuth 2.0 and configure a client in the ADOGRC Administration:
Go to Authentication > OAuth 2.0.
Select Enabled.
Click Create to add a new client. The Client box appears. Adapt the following parameters:
Type: Select the client type. Confidential clients are e.g. centralized, server based applications, which are capable of securely storing client secrets. Public clients are e.g. purely client based applications and native apps which are not capable of securely storing client secrets.
ID: The ID of the client system. Must be unique among the clients, should be kept simple as special characters need to be URL encoded.
Name: The name of the client application. Will be shown on the user interface.
Redirect URI: The URL of a redirect endpoint inside the client application which will be called by the authorization server when issuing an authorization code.
noteThe Redirect URI is unnecessary when using the Client Credentials Flow, however the Client Data form requires this field to be filled (mandatory for Authorization Code Flow).
Logo: Upload a logo to represent the client application. Will be shown on the user interface.
Access token validity (seconds): The time in seconds how long an access token is valid until it expires. Default: 1800s = 30 minutes.
Refresh token validity (seconds): The time in seconds how long a refresh token is valid until it expires. Default: 1209600s = 14 days.
Secret: The secret to use for client authentication. You can click Generate to generate a new secret or manually specify one.
Back on the OAuth 2.0 page, click Save. Now you can call the SCIM API with OAuth 2.0 authentication.
Configure OIDC Authentication
You need to enable OIDC authentication in the SCIM Services settings (see Configure Settings for OIDC) and in the OIDC settings (see Enable OIDC for ADOGRC).
OpenID Connect (OIDC) is an identity layer built on top of OAuth 2.0 and is suitable for secure authentication scenarios where identity tokens are required. Ensure your Identity Provider supports OIDC and is correctly configured for SCIM integration.
Configure Settings for OIDC
To enable OIDC authentication for SCIM services:
Go to Settings > SCIM Services > General > OIDC.
Select Enable OIDC.
Enable OIDC for ADOGRC
For security reasons, OIDC authentication is turned off by default in ADOGRC. If you want to use SCIM services with OIDC, you need to enable OIDC and configure a client in the ADOGRC Administration:
Go to Authentication > OIDC.
Select Enabled.
Click Create to add a new client. The Client box appears. Adapt the following parameters:
Type: Select the client type. Confidential clients are, for example, server-based applications capable of securely storing secrets. Public clients include native apps or browser-based apps which cannot securely store secrets.
ID: The unique identifier for the client application. Should be kept simple, as special characters must be URL encoded.
Name: The display name of the client application. This name may be shown to users during login.
Redirect URI: The redirect endpoint of the client application. This is where ADOGRC will send the user after successful authentication, along with the authorization code.
Logo: Optionally upload a logo to visually represent the client application in the user interface.
Access token validity (seconds): The duration in seconds for which an access token remains valid. Default: 1800 seconds (30 minutes).
Refresh token validity (seconds): The duration in seconds for which a refresh token remains valid. Default: 1209600 seconds (14 days).
ID token validity (seconds): The duration in seconds for which an ID token remains valid. Default: 36000 seconds (10 hours).
Preauthorized scopes: Select the scopes that should be automatically approved without requiring user interaction. Authorization requests containing only these scopes are granted immediately if the user is already logged in, without showing a consent dialog. Requests that include scopes not listed here will still require the user’s explicit consent. This setting is particularly useful in scenarios such as microfrontends, where seamless access without repeated authorization is desired.
Secret: The client secret used for authentication. You can manually enter a value or click Generate to create a new one automatically.
Back on the OIDC page, click Save. Now you can call the SCIM API with OIDC authentication.
Configure JWT Authentication
You need to enable JWT authentication in the SCIM Services settings (see Configure Settings for JWT Authentication) and in the JWT (REST) settings (see Enable JWT Authentication for ADOGRC).
JWT authentication is a secure and modern authentication method suitable for integration with external identity providers that issue signed tokens.
Configure Settings for JWT Authentication
To configure JWT authentication for SCIM services:
Go to Settings > SCIM Services > General > JWT.
Select Enable JWT.
Enable JWT Authentication for ADOGRC
For security reasons, JWT authentication is turned off by default in ADOGRC. To configure the SCIM API to accept a JSON Web Token (JWT) from an Identity Provider (IdP) for authentication, you need to adjust settings in the ADOGRC Administration:
Go to Authentication > JWT.
Select Enabled.
Click Create to add a new configuration. The Create JWT configuration box appears. Edit the properties to match your token:
: Name
Represents the identifier of this configuration.: Claim validation
A set of claims that need to be contained in the payload of the token. The "iss" (issuer)
claim identifies the JWT issuer (required). The "aud" (audience) claim identifies the
intended recipient of the token (optional).: Signature validation
A set of parameters that can be used for JWT signature validation. Which of these parameters
is required depends on the algorithm used to generate the signature in the header of the
token. At least one parameter needs to be configured.HMAC shared secret: Base64 encoded shared secret. Used in HS256, HS384 and HS512 signing algorithms.
JWKS URI: URL of the authorization server's JWK set, it contains the signing key(s) the client should use to validate signatures from the authorization server.
OIDC URI: URL of the OpenID Connect metadata provider as it is specified in OpenID Connect Discovery 1.0.
RSA public key: Base64 encoded public key. Used in RS256, RS384, RS512, PS256, PS384 and PS512 signing algorithms.
ECDSA public key: Base64 encoded public key. Used in ES256, ES384 and ES512 signing algorithms.
: User mapping claim
A claim that needs to be contained in the payload of the token. This claim identifies the
user you wish to authenticate. The value of this claim must match the *user name* of a user
in ADOGRC (must have *Trusted Login*).
Back on the JWT page, click Save. Now you can call the SCIM API with JWT authentication. Add your JWT to the authorization header, formatted as Bearer.
Configure Token Based Authentication
To configure token based authentication for SCIM services:
Go to Settings > SCIM Services > General > Tokens.
Click Add context to define at least one security context (see below).
Token based authentication is a BOC Group proprietary authentication method which allows access to the SCIM API on behalf of a user by providing a token instead of a username and password. This authentication method is available for Java client applications only.
Define Security Context
You need to define at least one security context for token based authentication:
Add Context: To add a new security context, click Add context.
Edit or Delete Context: To the right of the security context, click
More, and then click Editor Delete.
A security context consists of the following parts:
key
secret
technical user
SCIM services support multiple security contexts. At least one security context is required.
When would you want to use multiple security contexts? You can execute requests with access rights of different technical users. During execution, you can choose which of the predefined security contexts should be used.
Let's take a detailed look at the settings:
Key (for authentication by target system): This parameter represents the name of the key which is used for communication with the web application using authenticated REST APIs. Enter a descriptive name, e.g. "boc.rest.key.mfb.SCIMServices".
Secret (for authentication by target system): This parameter represents the secret value of the key which is used for communication with the web application using authenticated REST APIs. Click Generate secret to generate the value of the key.
Technical user: Select the technical user you created, i.e. "Technical_SCIMServices" (see Create Technical User).
More
In this section:
SCIM Default User Group
A special user group in ADOGRC supports user provisioning: the SCIM Default User Group.
This group is created automatically when the Enable SCIM Services globally option is activated (see Activate Access to the SCIM Services) and the ADOGRC application server is restarted.
When users are provisioned from an Identity Provider (IdP) into ADOGRC without group information, they are placed in this group. If group information is provided in a later provisioning, the user's group membership is updated accordingly.
If a user is removed from their last group during provisioning, they are moved to the SCIM Default User Group.
The user executing the provisioning must have permissions for the SCIM Default User Group (see User Account for Provisioning).
User Account for Provisioning
The user account in ADOGRC under whose context SCIM requests are executed must meet specific requirements:
The user must have Write permissions for the SCIM Default User Group and any other user groups to which users are provisioned in ADOGRC.
- These permissions can be assigned by a ADOGRC administrator in the ADOGRC Administration, on the Rights page under the Users tab (see View or Change Permissions).
The user context for executing SCIM requests depends on the configured authentication method:
Basic Authentication: The user whose username and password are sent Base64-encoded in the HTTP authorization header.
OAuth 2.0 Authentication
Authorization Code Flow: The user who authenticated and issued the access token.
Client Credentials Flow: The technical user associated with the configured scope.
OIDC Authentication: The user who authenticated and issued the access token.
JWT Authentication: The user identified via the claim (e.g., sub) in the validated JWT token.
Token-Based Authentication: The technical user associated with the configured key and secret.
REST API
ADOGRC offers a generic, extensible REST API that allows authenticated access to exposed functionality. The REST API can be used to e.g. send GET requests to query ADOGRC for data.
The availability of this feature depends on the licence. Access to the application programming interface (API) is limited to 500 requests per hour.
Activate Access to the REST API
Instructions on how to activate access to the REST API are covered here in the Administration Help.
You must first perform the following steps:
Create Technical User (required for OAuth 2.0 using the Client Credentials Flow and token based authentication only)
Then you can configure the authentication method you want to use to communicate with the REST API:
These steps are explained in the following sections.
Need help deciding on a suitable authentication method? Check out Choosing an Authentication Method for a short overview of each method.
Use the REST API
For information on how to use the REST API, please refer to the BOC Developer Portal.
Create Technical User
Do you want to use OAuth 2.0 authentication using the Client Credentials Flow to authenticate requests to the REST API, or token based authentication? If yes, you need to create a technical user now.
A technical user is NOT necessary for basic authentication, OAuth 2.0 authentication using the Authorization Code Flow and JWT authentication.
To create the technical user in the ADOGRC Administration:
Go to the Users page and click New User.
Begin by filling out the account details on the General tab:
Enter a name for the technical user, e.g. "Technical_StandardRESTfulServices".
Enter and confirm a password of your choice.
Next, go to the Groups and roles tab:
- Under User groups, click Select user groups and assign the user to the Default group.
Next, go to the Repository tab:
- Click Select repository and only (!) assign the repository to the user which holds the data to be queried.
Click Create to complete the user creation process.
Once user creation is complete, you can enable trusted login for the user:
Hover over the user, click
More, and then select Edit.
On the General tab, under Trusted login, select Enabled.
Assign Access Rights to the ADOGRC Administration
If you want to use user write APIs, you must assign access rights to the ADOGRC Administration to the user in whose context requests should be executed.
This can either be the technical user (for OAuth 2.0 authentication using the Client Credentials Flow and token based authentication) or any ADOGRC user (for basic authentication, OAuth 2.0 authentication using the Authorization Code Flow and JWT authentication).
To assign access rights to the ADOGRC Administration:
Go to the Rights page.
In the Users / Groups catalogue on the left, select the user to whom you want to grant access rights to the ADOGRC Administration.
Go to the Components tab.
In the workspace, find the "Administration Toolkit" component.
In the Access column, click
Change Permissions, and then choose Access.
Edit System Settings
Now you have to define a few technical settings controlling the base functionality of ADOGRC in the ADOGRC Administration. To edit the System settings:
Go to Settings > System settings > System.
The Base URL field must contain the URL where ADOGRC can be reached from other machines.
Do you want to use OAuth 2.0 authentication using the Client Credentials Flow or token based authentication? If yes, click Select users and select the technical user you created, e.g. "Technical_StandardRESTfulServices" (see Create Technical User).
Click Save.
Base URL Example
You are configuring ADOGRC 14. The IP address of the Tomcat server is 10.2.100.68 and the port is 8000. The URL should look like this
"http://10.2.100.68:8000/ADONIS17_0"
Configure General Settings
Now the general settings for the REST API have to be adapted in the ADOGRC Administration:
- Go to Settings > Standard RESTful Services > General.
These settings apply to all authentication methods:
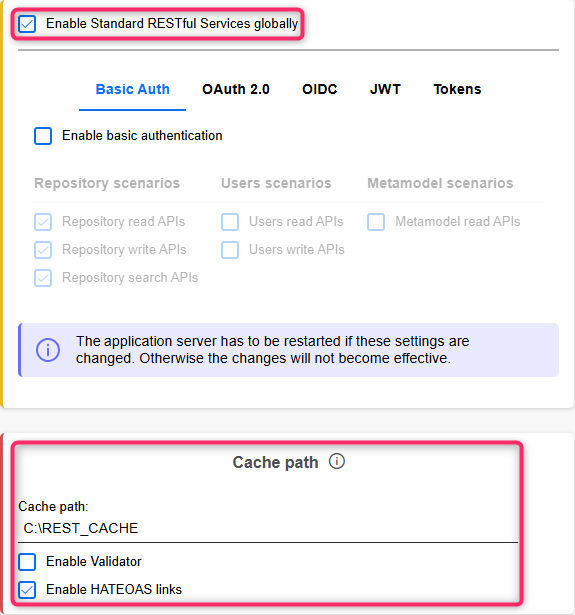
Enable Standard RESTful Services globally: Select this option to enable the REST API. All other settings in this area are inactive unless you select this option.
Cache Path: This parameter is optional. Enter the absolute path to the directory in which cache files must be stored. The user under which the Apache Tomcat web server service is running must have write access to this directory. If the directory does not exist, it will be created by ADOGRC.
Advantages of using the Cache Path parameter:
Model images and model image maps are generated only once and then cached. Every time the model image or image map is requested, a check is performed if the model has changed. If there are no changes, the information is loaded from the file system. Otherwise, the cache is updated first. As a result, responses to these types of requests are faster and use fewer server resources.
For search jobs the advantage is that created queries are saved in cache files and can be reused after a server restart. Without the cache path, queries are saved only in memory and are lost during restart.
Enable Validator: This parameter is optional. Select this option to turn on syntax and semantic validation of XML and JSON responses. Enabling this parameter may slow down the execution of requests and cause high memory consumption and CPU usage on the web server.
Enable HATEOAS links: This parameter is enabled by default. When you clear this option, responses to requests will not include HATEOAS links that help you find related resources.
Configure Basic Authentication
You need to enable basic authentication in the Standard RESTful Services settings (see Configure Settings for Basic Authentication) and in the Security settings (see Enable Basic Authentication for ADOGRC).
Configure Settings for Basic Authentication
To configure basic authentication for the REST API in the ADOGRC Administration:
Go to Settings > Standard RESTful Services > General.
Edit the settings on the Basic Auth tab.
The following settings are available:
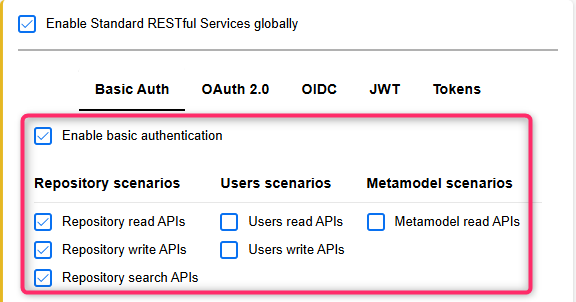
- Enable Basic Authentication: Select this option to enable basic authentication. All other settings in this tab are inactive unless you select this option.
- Repository scenarios | Users scenarios | Metamodel scenarios: In this area, you can enable specific REST scenarios. If a scenario is not enabled, all requests to its endpoints will return a 403 FORBIDDEN status. HATEOAS links that help you find related resources are also affected. For example, the response to a request to get user information may contain a HATEOAS link to delete the user. If the user write APIs scenario is disabled, a request to this link will return the status code 403 FORBIDDEN.
To find out which endpoints are assigned to the REST scenarios, see the API Reference in the BOC Developer Portal where they are grouped according to the scenarios.
Enable Basic Authentication for ADOGRC
For security reasons, basic authentication is turned off by default in ADOGRC. If you want to use the REST API with basic authentication, you need to adapt the Security settings in the ADOGRC Administration:
Go to Authentication > More options, and then click Security Settings.
Switch to the REST tab.
Adapt the following settings:
- Basicauth IP Restrictions: Specify the IP addresses that shall be allowed to send requests with basic authentication to the REST API (see Configure IP Restrictions for more information).
- Basicauth Roles: This setting is optional. Select system roles that a user must have at least one of in order to use the ADOGRC REST API with basic authentication. If no system role is selected, all system roles will allow access to the API.
No restart is required when modifying these settings.
Configure OAuth 2.0 Authentication
You need to enable OAuth 2.0 authentication in the Standard RESTful Services settings (see Configure Settings for OAuth 2.0) and in the OAuth 2.0 settings (see Enable OAuth 2.0 for ADOGRC).
Configure Settings for OAuth 2.0
To configure OAuth 2.0 authentication for the REST API in the ADOGRC Administration:
Go to Settings > Standard RESTful Services > General.
Edit the settings on the OAuth 2.0 tab.
The following settings are available:
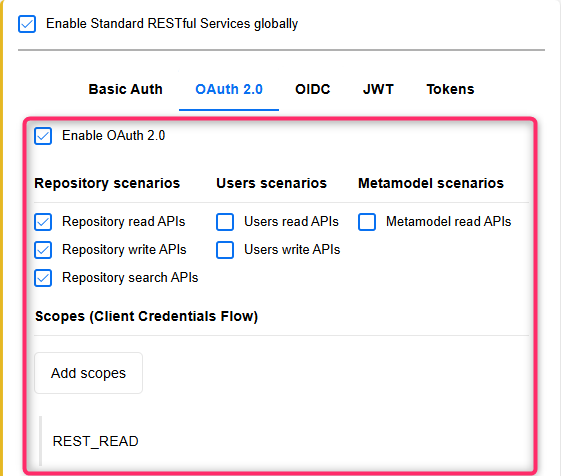
- Enable OAuth 2.0: Select this option to enable OAuth 2.0 authentication. All other settings in this tab are inactive unless you select this option.
- Repository scenarios | Users scenarios | Metamodel scenarios: In this area, you can enable specific REST scenarios. If a scenario is not enabled, all requests to its endpoints will return a 403 FORBIDDEN status. HATEOAS links that help you find related resources are also affected. For example, the response to a request to get user information may contain a HATEOAS link to delete the user. If the user write APIs scenario is disabled, a request to this link will return the status code 403 FORBIDDEN.
To find out which endpoints are assigned to the REST scenarios, see the API Reference in the BOC Developer Portal where they are grouped according to the scenarios.
Scopes (Client Credentials Flow)
OAuth 2.0 offers multiple flows. ADOGRC supports the Authorization Code Flow and the Client Credentials Flow.
Do you want to use the Client Credentials Flow? If yes, you need to define at least one scope:
Add Scope: To add a new scope, click Add scopes.
Edit or Delete Scope: To the right of the scope, click
More, and then click Edit or Delete.
A scope consists of the following parts:
name
IP constraints
technical user
ADOGRC RESTful services support multiple scopes. At least one scope is required.
When would you want to use multiple scopes? You can execute requests with access rights of different technical users or from different IP ranges. During execution, you can choose which of the predefined scopes should be used.
Let's take a detailed look at the settings:
Name: This parameter represents the name of the scope. Enter a descriptive name, e.g. "REST_READ".
IP constraints: This parameter is optional. You can restrict the IP addresses that shall be able to access a scope by passing an IP constraint pattern. Here's how the configuration works:
An IP constraint consists of a comma separated list of rules.
A rule consists of a keyword ('allow' or 'deny') followed by a white space, and an IP address or address with wild card * (e.g. 192.168.*). The keyword "all" can be used to match all addresses.
If rules are present, but no match is made, the default setting is "deny".
If no rules are present, the default setting is "allow".
The first matching rule decides. E.g. when you formulate a constraint like "allow 192.*, deny 192.168.0.1", the 'deny' rule would have no effect, as that address matches the 'allow' rule already.
Example
Deny all IP addresses starting with 192., deny the IP address 193.168.0.1, allow all other IP addresses:
deny 192.*,deny 193.168.0.1,allow all
Allow all IP addresses starting with 178. except 178.6.6.6, deny all other IP addresses:
deny 178.6.6.6,allow 178.*
- Technical user: Select the technical user you created, e.g. "Technical_StandardRESTfulServices" (see Create Technical User).
Enable OAuth 2.0 for ADOGRC
If you want to use the REST API with OAuth 2.0, you need to enable OAuth 2.0 and configure a client in the ADOGRC Administration:
- Go to Authentication > OAuth 2.0.
The necessary settings are described below.
Enable OAuth 2.0 Authentication for ADOGRC
For security reasons, OAuth 2.0 authentication is turned off by default in ADOGRC. To enable OAuth 2.0 authentication:
- Select Enabled.
Add and Configure Client
Next, you will need to add a new client:
- Click Create to add a new client. The Client box appears.
Adapt the following parameters:
Type: Select the client type. Confidential clients are e.g. centralized, server based applications, which are capable of securely storing client secrets. Public clients are e.g. purely client based applications and native apps which are not capable of securely storing client secrets.
ID: The ID of the client system. Must be unique among the clients, should be kept simple as special characters need to be URL encoded.
Name: The name of the client application. Will be shown on the user interface.
Redirect URI: The URL of a redirect endpoint inside the client application which will be called by the authorization server when issuing an authorization code.
The Redirect URI is unnecessary when using the Client Credentials Flow, however the Client Data form requires this field to be filled (mandatory for Authorization Code Flow).
Logo: Upload a logo to represent the client application. Will be shown on the user interface.
Access token validity (seconds): The time in seconds how long an access token is valid until it expires. Default: 1800s = 30 minutes.
Refresh token validity (seconds): The time in seconds how long a refresh token is valid until it expires. Default: 1209600s = 14 days.
Secret: The secret to use for client authentication. You can click Generate to generate a new secret or manually specify one.
Back on the OAuth 2.0 page, click Save. Now you can call the REST API with OAuth 2.0 authentication.
Configure OIDC Authentication
You need to enable OIDC authentication in the Standard RESTful Services settings (see Configure Settings for OIDC) and in the OIDC settings (see Enable OIDC for ADOGRC).
Configure Settings for OIDC
To configure OIDC authentication for the REST API in the ADOGRC Administration:
Go to Settings > Standard RESTful Services > General.
Edit the settings on the OIDC tab.
The following settings are available:
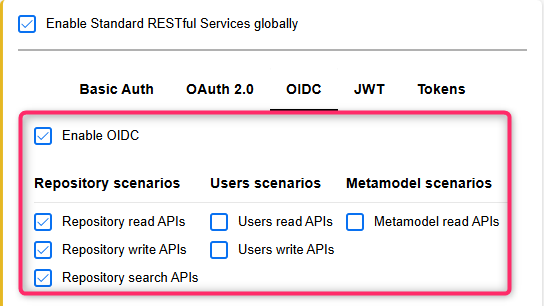
- Enable OIDC: Select this option to enable OIDC authentication. All other settings in this tab are inactive unless you select this option.
- Repository scenarios | Users scenarios | Metamodel scenarios: In this area, you can enable specific REST scenarios. If a scenario is not enabled, all requests to its endpoints will return a 403 FORBIDDEN status. HATEOAS links that help you find related resources are also affected. For example, the response to a request to get user information may contain a HATEOAS link to delete the user. If the user write APIs scenario is disabled, a request to this link will return the status code 403 FORBIDDEN.
To find out which endpoints are assigned to the REST scenarios, see the API Reference in the BOC Developer Portal where they are grouped according to the scenarios.
Enable OIDC for ADOGRC
If you want to use the REST API with OIDC, you need to enable OIDC and configure a client in the ADOGRC Administration:
- Go to Authentication > OIDC.
The necessary settings are described below.
Enable OIDC Authentication for ADOGRC
For security reasons, OIDC authentication is turned off by default in ADOGRC. To enable OIDC authentication:
- Select Enabled.
Add and Configure Client
Next, you will need to add a new client:
- Click Create to add a new client. The Client box appears.
Adapt the following parameters:
Type: Select the client type. Confidential clients are, for example, server-based applications capable of securely storing secrets. Public clients include native apps or browser-based apps which cannot securely store secrets.
ID: The unique identifier for the client application. Should be kept simple, as special characters must be URL encoded.
Name: The display name of the client application. This name may be shown to users during login.
Redirect URI: The redirect endpoint of the client application. This is where ADOGRC will send the user after successful authentication, along with the authorization code.
Logo: Optionally upload a logo to visually represent the client application in the user interface.
Access token validity (seconds): The duration in seconds for which an access token remains valid. Default: 1800 seconds (30 minutes).
Refresh token validity (seconds): The duration in seconds for which a refresh token remains valid. Default: 1209600 seconds (14 days).
ID token validity (seconds): The duration in seconds for which an ID token remains valid. Default: 36000 seconds (10 hours).
Preauthorized scopes: Select the scopes that should be automatically approved without requiring user interaction. Authorization requests containing only these scopes are granted immediately if the user is already logged in, without showing a consent dialog. Requests that include scopes not listed here will still require the user’s explicit consent. This setting is particularly useful in scenarios such as microfrontends, where seamless access without repeated authorization is desired.
Secret: The client secret used for authentication. You can manually enter a value or click Generate to create a new one automatically.
Back on the OIDC page, click Save. Now you can call the REST API with OIDC authentication.
Configure JWT Authentication
You need to enable JWT authentication in the Standard RESTful Services settings (see Configure Settings for JWT Authentication) and in the JWT (REST) settings (see Enable JWT Authentication for ADOGRC).
Configure Settings for JWT Authentication
To configure JWT authentication for the REST API in the ADOGRC Administration:
Go to Settings > Standard RESTful Services > General.
Edit the settings on the JWT tab.
The following settings are available:
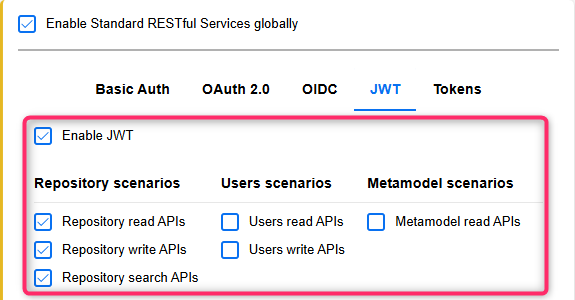
- Enable JWT: Select this option to enable JWT authentication. All other settings in this tab are inactive unless you select this option.
- Repository scenarios | Users scenarios | Metamodel scenarios: In this area, you can enable specific REST scenarios. If a scenario is not enabled, all requests to its endpoints will return a 403 FORBIDDEN status. HATEOAS links that help you find related resources are also affected. For example, the response to a request to get user information may contain a HATEOAS link to delete the user. If the user write APIs scenario is disabled, a request to this link will return the status code 403 FORBIDDEN.
To find out which endpoints are assigned to the REST scenarios, see the API Reference in the BOC Developer Portal where they are grouped according to the scenarios.
Enable JWT Authentication for ADOGRC
To configure the ADOGRC REST API to accept a JSON Web Token (JWT) from an Identity Provider (IdP) for authentication, you need to adjust settings in the ADOGRC Administration:
- Go to Authentication > JWT.
The necessary settings are described below.
Enable JWT Authentication for ADOGRC
For security reasons, JWT authentication is turned off by default in ADOGRC. To enable JWT authentication:
- Select Enabled.
Create JWT Configuration
Next, you will need to add a new JWT configuration and edit the properties to match your token:
- Click Create to add a new configuration. The Create JWT configuration box appears.
Adapt the following parameters:
Name: Represents the identifier of this configuration.
Claim validation: A set of claims that need to be contained in the payload of the token. The "iss" (issuer) claim identifies the JWT issuer (required). The "aud" (audience) claim identifies the intended recipient of the token (optional).
Signature validation: A set of parameters that can be used for JWT signature validation. Which of these parameters is required depends on the algorithm used to generate the signature in the header of the token. At least one parameter needs to be configured.
HMAC shared secret: Base64 encoded shared secret. Used in HS256, HS384 and HS512 signing algorithms.
JWKS URI: URL of the authorization server's JWK set, it contains the signing key(s) the client should use to validate signatures from the authorization server.
OIDC URI: URL of the OpenID Connect metadata provider as it is specified in OpenID Connect Discovery 1.0.
RSA public key: Base64 encoded public key. Used in RS256, RS384, RS512, PS256, PS384 and PS512 signing algorithms.
ECDSA public key: Base64 encoded public key. Used in ES256, ES384 and ES512 signing algorithms.
User mapping claim: A claim that needs to be contained in the payload of the token. This claim identifies the user you wish to authenticate. The value of this claim must match the user name of a user in ADOGRC (must have Trusted Login).
Back on the JWT page, click Save. Now you can call the REST API with JWT authentication. Add your JWT to the authorization header, formatted as Bearer.
Configure Token Based Authentication
To configure token based authentication for the REST API in the ADOGRC Administration:
Go to Settings > Standard RESTful Services > General.
Edit the settings on the Tokens tab.
The following settings are available:
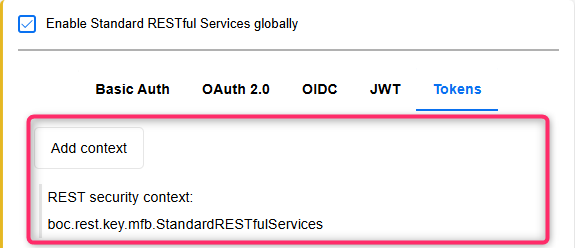
Define REST Security Context
You need to define at least one REST security context for token based authentication:
Add Context: To add a new security context, click Add context.
Edit or Delete Context: To the right of the security context, click
More, and then click Editor Delete.
A security context consists of the following parts:
key
secret
technical user
REST scenarios
ADOGRC RESTful services support multiple security contexts. At least one security context is required.
When would you want to use multiple security contexts? For example, you can configure one security context that allows for modification of users, and another one with access to the repository. You can execute requests with access rights of different technical users. During execution, you can choose which of the predefined security contexts should be used.
Let's take a detailed look at the settings:
Key (for authentication by target system): This parameter represents the name of the key which is used for communication with the web application using authenticated REST APIs. Enter a descriptive name, e.g. "boc.rest.key.mfb.StandardRESTfulServices".
Secret (for authentication by target system): This parameter represents the secret value of the key which is used for communication with the web application using authenticated REST APIs. Click Generate secret to generate the value of the key.
Technical user: Select the technical user you created, i.e. "Technical_StandardRESTfulServices" (see Create Technical User).
Repository scenarios | Users scenarios | Metamodel scenarios: In this area, you can enable specific REST scenarios. If a scenario is not enabled, all requests to its endpoints will return a 403 FORBIDDEN status. HATEOAS links that help you find related resources are also affected. For example, the response to a request to get user information may contain a HATEOAS link to delete the user. If the user write APIs scenario is disabled, a request to this link will return the status code 403 FORBIDDEN.
To find out which endpoints are assigned to the REST scenarios, see the API Reference in the BOC Developer Portal where they are grouped according to the scenarios.
Choosing an Authentication Method
ADOGRC offers a range of authentication methods to secure communication with its REST API. Your choice of authentication method may depend on various factors, including security requirements, existing infrastructure, and the capabilities of your client applications. This section offers a short overview of each method to assist you in choosing the most suitable authentication approach.
Basic Authentication
Basic authentication is the most simple method for authentication. It involves sending a username and password with each request. These credentials are Base64-encoded and sent in the HTTP authorization header.
A technical user is NOT necessary for basic authentication. Requests may be executed in the context of any standard product user.
While straightforward, it is crucial to ensure secure transmission. As the credentials are only encoded and not encrypted, it is highly recommended to use basic authentication only in conjunction with HTTPS, i.e. the Tomcat server on which the ADOGRC web application is deployed needs to be configured to use SSL/TLS as described in the ADONIS Installation Manual to encrypt the communication between the client and the web server.
When to Use Basic Authentication
Basic authentication proves to be a suitable choice for testing purposes and for client applications that require a simple authentication method and need to authenticate users swiftly and effortlessly. It serves well for client applications where a user needs to log in before access to specific resources is possible.
OAuth 2.0 Authentication
OAuth 2.0 authentication offers a flexible and secure authorization framework, allowing access to the REST API on behalf of a user without requiring the user's password. Instead, each request is accompanied by an access token to confirm the identity of the user and ensure the validity of the request. The actual authentication of the user is delegated to an external identity provider (IdP).
Two primary flows can be configured:
Authorization Code Flow: Suitable for scenarios where user consent is required. A technical user is NOT necessary. Requests may be executed in the context of any standard product user.
Client Credentials Flow: Ideal for machine-to-machine (M2M) communication without user involvement. A technical user needs to be created. Requests are executed in the context of this technical user.
When to Use OAuth 2.0 Authentication
OAuth 2.0 authentication is commonly used in scenarios where third-party applications need limited access to ADOGRC on behalf of a user. Proving a secure and standardized way for applications to obtain access with the user's consent, it allows for granular control over the level of access granted.
OIDC Authentication
OpenID Connect (OIDC) authentication builds on the OAuth 2.0 protocol and adds an identity layer on top. It allows client applications to authenticate users based on identity tokens issued by a trusted identity provider (IdP).
In the context of ADOGRC, ADOGRC itself acts as the OpenID Provider (OP), issuing identity tokens to client applications that support OIDC authentication.
A technical user is NOT necessary for OIDC authentication. Requests may be executed in the context of any standard product user.
OIDC is particularly useful in scenarios where external applications need to authenticate users and also retrieve user identity and authorization information using standardised claims included in the token. This can include, for example, role or group membership data that the client application can evaluate. As with other authentication methods, ensure secure communication by enabling HTTPS.
When to Use OIDC Authentication
OIDC authentication is recommended when a client application integrates with the ADOGRC REST API and needs to access its functionality on behalf of authenticated users while also evaluating their authorisation. This includes use cases where the application checks, for example, whether a user belongs to a specific group or has a required role.
JWT Authentication
JWT authentication enables the use of an external identity provider (IdP) for user authentication. Once the user has acquired a JSON Web Token (JWT) from the IdP, they can include it in requests in the HTTP authorization header as a bearer token. ADOGRC will validate the JWT to determine whether the client has the necessary permissions to access the resource.
A technical user is NOT necessary for JWT authentication. Requests may be executed in the context of any standard product user.
Compact, self-contained, and supporting digital signatures for added security, JWTs can include additional information (claims) beyond authentication.
When to Use JWT Authentication
JWT authentication is considered a flexible, secure, and scalable approach. If security is a top priority and additional features like statelessness and additional claims are needed, JWT authentication may be the best choice for your client application.
Token Based Authentication
Token based authentication is a BOC Group proprietary authentication method which allows access to the REST API on behalf of a user by providing a token instead of a username and password. It involves sending a security hash which is constructed using a public identifier of the client, a secret key of the client, a GUID, a timestamp of the request and the parameters sent with the request. This prevents unauthorized usage of the API as well as repeated transmission and other abuse of requests.
A technical user needs to be created for token based authentication. Requests are executed in the context of this technical user.
This authentication method is available for Java client applications only.
When to Use Token Based Authentication
The BOC Group is charting a course to mark this authentication method as deprecated in the future. As a result, we encourage users to explore alternative authentication methods for a sustainable and future-proof approach.
System Settings
In this area you manage the following configuration options for ADOGRC:
Active Features
The settings for active features impact the fundamental behaviour of ADOGRC.
Open Settings for Active Features
To open the settings for active features:
- Go to Settings > System settings > Active features.
Configure Settings for Active Features
The following settings are available:
Allow renaming of catalogue elements: Select this option to allow renaming of catalogue elements displayed in ADOGRC.
Allow creation of new objects: Select this option to allow creating new objects in ADOGRC via the catalogue or via relations controls.
Hide model types when creating new objects: Select this option to display all object types in a flat list when creating an object in the Explorer. When you clear this option, object types are grouped by model type.
Allow creation of model groups: Select this option to allow creating new model groups in ADOGRC via the catalogue.
Allow creation of object groups: Select this option to allow creating new object groups in ADOGRC via the catalogue.
Allow moving elements in the catalogue: Select this option to allow ADOGRC users to move elements (models, objects, groups) to other parent folders using drag and drop.
Allow deletion of models and objects: Select this option to allow deleting models and objects in ADOGRC via the catalogue or via relations controls.
Allow models of same type and with same name: Select this option to allow ADOGRC users to create multiple models of the same type with the same name.
Allow repository objects of same class and with same name: Select this option to allow ADOGRC users to create multiple repository objects of the same type with the same name.
Show models in the catalogue: Select this option to show models in the catalogue of ADOGRC.
Show objects in the catalogue: Select this option to show objects in the catalogue of ADOGRC.
Enable collaboration component: Select this option to allow using the collaboration component in ADOGRC.
Enable dependency analyser component: Select this option to allow using the dependency modeller component in ADOGRC. Additional configuration steps may be needed.
Enable favourites component: Select this option to allow using favourites in ADOGRC.
Enable translation component: Select this option to allow using the translation component in ADOGRC.
Enable file upload to DMS: Select this option to allow importing external files into the database in ADOGRC.
Enable graphical model comparison: Select this option to allow using the graphical model comparison in ADOGRC.
Enable change password: Select this option to allow changing the password in ADOGRC.
Enable recently opened models: Select this option to display recently opened models in the Quick Access component in the Explorer. When you clear this option, models are not displayed in Quick Access.
Enable recently opened objects: Select this option to display recently opened objects in the Quick Access component in the Explorer. When you clear this option, objects are not displayed in Quick Access.
Search automatically activated: Select this option to activate the setting Search automatically in ADOGRC by default, i.e. the search results are automatically adjusted whenever the user edits a search filter.
Deactivate "Save As": Select this option to disallow creating copies of models in ADOGRC.
Activate highlighting for relations: Select this option to highlight the relation with the highest priority when creating relations in ADOGRC. When you clear this option, no relation is highlighted.
The ADOGRC application server has to be restarted if these settings are changed. Otherwise the changes will not become effective.
Email
ADOGRC includes a mail component, which can be used to send messages automatically on several events. Before it is possible to use this component, it has to be configured correctly.
Open Settings for the Email Service
To open the settings for the email service:
- Go to Settings > System settings > Email.
Settings for the Email Service
The following settings are available:
Activate email service: Select this option to activate the email service. When the web server is started, it will regularly poll the application server for new emails.
IP address or name of the email server: Enter the IP address or the host name of the client where the email server is installed.
Port of the email server: Enter the port number which is used to access the email server. Normally this is port 25.
System sender address: Enter the email address which should be used as sender address for system notifications (e.g. users receive a notification when their attention is required for a step in a release workflow, and the sender address is the system address entered in this field).
System replyTo: Enter the email address to which replies for system notifications should be sent (if replies should not be sent to the system sender address).
Encryption: Select an encryption option if the email server requires it. The following settings are available:
None: No encryption is used.
StartTLS (optional): Use StartTLS to upgrade to a secure connection. If the email server does not support StartTLS, an unencrypted connection is used.
StartTLS (required): Use StartTLS to upgrade to a secure connection. If the email server does not support StartTLS, the operation will fail (= emails are not sent).
SSL/TLS: Use SSL or TLS to encrypt communication. If the email server does not support SSL/TLS, the operation will fail (= emails are not sent).
Authentication Type: Choose the authentication method required by your email service.
None: Select this option if the email server does not require authentication.
Basic: If the email server uses basic authentication, enter the following credentials:
Username: Enter the username for the email account.
Password: Enter the corresponding password.
OAuth2: If your email service requires OAuth 2.0 authentication, provide the following details:
Username: Enter the username for the email account.
Client ID: Provide the OAuth2 client ID assigned to your application.
Secret: Enter the OAuth2 client secret.
Token Endpoint URL: Provide the URL used to obtain an OAuth2 access token.
Scope: Define the required scope for email sending permissions.
Interval in seconds for processing emails: This setting defines the interval that is used by the web server to poll the application server for new emails. A value of 300 means that the web server will wait for 300 seconds (= 5 minutes) between requests for new emails.
Maximum number of failed send attempts (0=unlimited): Specifies the number of send attempts after which emails that fail to send (e.g. because the email address does not exist anymore) are skipped.
Before it is possible to send email notifications, the Base URL has to be configured correctly.
The ADOGRC web application running on the web server has to be restarted if these settings are changed. Otherwise the changes will not become effective.
When does ADOGRC send emails?
ADOGRC sends emails in the following situations:
When someone shares a model, an object etc. directly from ADOGRC with colleagues.
As part of comments. Example: When someone is directly mentioned with @ in a comment, or if they are part of the discussion and someone else writes a new answer.
As part of release workflows. Example: After a transition, the person who is responsible for carrying out the next transition in the release process receives an email.
When a user resets their password with the self-service password reset.
ADOGRC provides a separate set of automatic background jobs which can check and prepare ADOGRC objects participating in one the ADOGRC workflows. Notifications for these workflows are sent by the ADOGRC Notifications Service. For details on how to configure these background jobs, see the chapter ADOGRC Technical Configuration.
For details on how to configure the self-service password reset please refer to section Configure Self-Service Password Reset.
File Management
As an ADOGRC administrator, you can control the types of files users and administrators are allowed to upload, set file size limits, and specify supported protocols for file pointer attributes.
Open File Management Settings
To open the file management settings:
- Go to Settings > System settings > File management.
Base
These settings apply to file uploads by users in ADOGRC. They serve as general defaults and are used unless more specific settings are defined for a particular upload functionality, such as when uploading documents or images.
Allowed file types for upload (space-separated extensions): Specify which file types users are permitted to upload by listing the allowed file extensions, separated by spaces. Default:
doc docx ppt pptx xls xlsx csv txt pdf rtf png jpggif jpeg bmp svg zip rar 7z axr xml bpmn avi tif
These types represent the full set ("superset") of formats supported by ADOGRC. More specific functionalities may define their own narrower subset. Any file types permitted in a specific context must also be included in this list.
For example, the settings for uploading documents (Document Management) only allow
the following types by default: doc docx ppt pptx xls xlsx txt pdf rtf png jpg gif.
- Maximal file size for upload (MB): Defines the maximum file size (in megabytes) that users are allowed to upload. Default:
50
If a more specific setting is defined for a functionality, it overrides this value. For example, the
image upload settings (Media Management) define a lower default limit of 10 MB.
Admin page
These settings apply to file uploads by administrators in the ADOGRC Administration, such as when importing migration packages. They follow the same logic as the Base settings described above, meaning they serve as general defaults unless more specific settings are defined for a particular upload functionality.
Allowed file types for upload (space-separated extensions): Defines an extended set of file types permitted for upload via the ADOGRC Administration. Default:
doc docx ppt pptx xls xlsx csv txt pdf rtf png jpg gif jpeg bmp svg zip rar 7z axr xml bpmn avi tif axm axs axl htm html jar mfb sk manifest csMaximal file size for upload (MB): Specifies a larger maximum file size to support administrative operations. Default:
10240(=10 GB)
The settings in the "Admin page" section apply to the following components of the ADOGRC Administration:
The following components use hardcoded upload settings and are not affected by this configuration:
File protocols
Administrators can define which URI protocols are permitted in file pointer attributes. These
protocols allow users to link to external files or systems from within ADOGRC. If a file pointer
uses a protocol not listed here, ADOGRC assumes the default file:/// protocol.
- Supported protocols for file links in file pointer attributes (space-separated protocol
identifiers): Enter the protocol identifiers (space-separated) that ADOGRC should recognize when handling file
links. Default:
http https ftp ftps db file Notes
Full-Text Search
As an ADOGRC administrator, you can configure a variety of full-text search settings for ADOGRC.
Open Full-Text Search Settings
To open the full-text search settings:
- Go to Settings > System settings > Full-text search.
Global Attributes
When using the general search function in ADOGRC (Search & Analysis), certain attributes are considered to find matching objects or models. By default, these are the attributes Name, Description, First name and Last name.
The settings in this area allow you to define additional attributes of the types Short String, ADOstring and Long String to consider.
Select attributes that should always be part of the search results: Select the attributes that should always be considered when using the general search function.
The search result table displays a separate column for each of these attributes. Found search terms are highlighted in yellow in the search result.
Search in Explorer
By default, only the Name is considered to find matching objects or models:
when using the search function in the Explorer
when adding relations in the properties of a model or object and using the search function
The settings in this area allow you to define additional aspects to consider.
- Apply global attributes for the search in explorer: Select this option so that the attributes selected in the Global Attributes area above are additionally considered when using the search function in the Explorer or when using the search function to add relations in the properties of a model or object.
Use name visualisation pattern for the search in Explorer: During the customising process of ADOGRC, a name pattern may be defined by a BOC Solution Engineer for a model type or class. The name pattern determines which components make up the visualised name on the user interface.
Select this option so that relations that are part of the defined name pattern are considered when using the search function in the Explorer or when using the search function to add relations in the properties of a model or object.
Example: Use name visualisation pattern for the search in Explorer
Suppose your organisation uses the following customised name visualisation pattern for models:
{NAME} [{RC_OWNER}]- Name and relation Process ownerFor example, if "Carol Process" is set as the Process owner of the "Create new customer" model, the visualised name on the user interface for the model will look like this:
Create new customer [carol]
Now, the option Use name visualisation pattern for the search in Explorer is selected. From this point forward, any models with "Carol Process" set as the Process owner will be found when searching in the Explorer with the phrase "carol". This also includes the Create new customer [carol] model mentioned above.
The ADOGRC application server has to be restarted if these settings are changed. Otherwise the changes will not become effective.
Model Comparison
Choose the properties to be evaluated during model comparison in ADOGRC. This tool makes the differences between two models visible. This includes deleted objects and connectors, new objects and connectors as well as changes in the property values. For example, this can be useful for identifying the differences between two versions of a process.
Open and Configure Model Comparison Settings
Go to Settings > System settings > Model comparison.
On the Model types, Classes and Relation classes tabs, select the properties to consider when comparing models. You can also use the search box to quickly find a specific property.
The ADOGRC application server has to be restarted if these settings are changed. Otherwise the changes will not become effective.
Modelling
Configure settings for automatic saving, visualisation options for ADOGRC and other settings. Most of these settings can be overridden by individual users of ADOGRC according to their preferences.
Open Modelling Settings
To open the modelling settings:
- Go to Settings > System settings > Modelling.
General Settings
The following settings are available:
- Autosave: Enable automatic saving of changes in models and objects. Determine the number of changes before the next autosave.
Modelling
The following settings are available:
Draw new connectors automatically in a rectangular manner: Make ADOGRC draw right-angled connectors
automatically. Clear this option to make ADOGRC draw straight connectors
instead.
Show bridges if connectors cross: Make ADOGRC draw bridges if connectors cross.
Show cross-hair when modelling: Show a crosshair when modelling.
Only move contained objects if Shift key is pressed: Resizable objects and aggregations can act as container objects for other objects. When you drag such a container around the drawing area, objects placed inside are moved along if you press and hold the <Shift> key at the same time.
Clear this option if you want contained objects to move along at all times (without simultaneously pressing the <Shift> key).
If you are using the ADOGRC Standard Application Library, the following object types are aggregations: Block, Group, System Boundary and the eponymous Aggregation.
Display page breaks & page numbers: Page breaks divide models into separate pages when you print. They are displayed as dashed lines in the graphical editor. Select whether page breaks and page numbers are visible, if a user has write access or read-only access to a model.
Activate web worker rendering: Web worker rendering means that model graphics are rendered in a separate process, which is more performant. When web worker rendering is disabled, the model is rendered in the same process as the rest of the client-side application, and graphics on the drawing area will load more slowly. Clear this option only if requested by a BOC employee.
Shrink model area only to the defined width and height of the model type: In the graphical editor, the model size automatically adapts to the model content. This means that the model area will expand or shrink as necessary to accommodate all objects.
Clear this option if you want the model area to expand as needed, but only shrink to the default dimensions specified for the model type in the metamodel, rather than the smallest possible size that still accommodates all objects.
Modelling Direction
The modelling direction can be set to horizontal (modelling is done from left to right) or vertical (modelling is done from top to bottom). You can define the modelling direction for each model type.
Select the Changeable option to allow ADOGRC users to change the modelling direction for a specific model in the graphical editor. The objects on the drawing area are automatically rearranged.
When using the Hover Modelling Assistant in ADOGRC, the modelling direction determines where the next object is placed:
Horizontal: To the right of the selected object
Vertical: Below the selected object
The ADOGRC application server has to be restarted if these settings are changed. Otherwise the changes will not become effective.
Modules
You can assign modules (plug-ins) to system roles to grant permissions for specific functionalities in ADOGRC. This allows you to define different scenarios for different user groups or users.
Open Modules Settings
To open the modules settings:
- Go to Settings > System settings > Modules.
View and Assign Modules
The modules settings present all modules that can be assigned to users in a table format. The following columns are displayed:
Name and description: Displays the name and, if available, a description of the module.
System roles: Identifies the system roles that have been granted access to the module.
Requires: Contains links to any other modules necessary for the proper functioning of the module.
Used By: Contains links to any other modules that use or depend on the module.
The following options are available:
Assign Modules: In the System roles column, select the system roles that should be granted access to the module. To grant access to all users, select the option Available for all users. If certain system roles are unavailable for selection, make sure that they have access to all required system roles.
Filter by System Roles: Click All roles, and then select the option you want. You can view modules Available for all users or only those available for specific system roles.
Search: In the Seach box, type the text you want to search for. All table rows containing the search string in the Name and description, Requires, or Used By columns will be displayed.
The ADOGRC application server has to be restarted if these settings are changed. Otherwise the changes will not become effective.
Error Message: Configured System Roles Could Not Be Found
The following situation can arise when importing component settings: In the import file, modules are assigned to system roles that do not exist in your database. Such system roles will be highlighted in red in the settings for modules. You can either recreate the missing system roles and make the assignment work again. Or you can remove the assignment (clear check box) and save the settings, and the system roles that do not exist in your database are removed from the configuration.
Object Mouseovers
Select the properties you want to display in object tooltips in ADOGRC. These tooltips provide contextual information when a user opens a read-only model in the graphical editor or in the Organisation Portal and hovers over an object.
Open and Configure Object Mouseovers Settings
Go to Settings > System settings > Object mouseovers.
Select the properties to display in object tooltips. You can also use the search box to quickly find a specific property.
The ADOGRC application server has to be restarted if these settings are changed. Otherwise the changes will not become effective.
Printing and Reporting
The printing and reporting settings allow configuring settings for printing models to PDF, creating PDF and RTF reports, and generating images in ADOGRC.
Open Printing and Reporting Settings
To open the printing and reporting settings:
- Go to Settings > System settings > Printing and reporting.
General Settings
The following settings are available:
- Default Page Layout: Select a default page layout for printing models to PDF and creating PDF and RTF reports. Page layouts determine the appearance of the header and footer.
If you are using the ADOGRC Standard Application Library, the default page layout for printing models to PDF is defined directly in the metamodel for all model types and this setting is not evaluated. This setting is however still evaluated as a default setting for creating reports.
ADOGRC users can choose their own preferred page layout for printing models to PDF and creating
reports (under > Preferences
> Printing).
- PDF Version: Select a PDF version for printing models to PDF and creating PDF reports. PDF is the default format for quality printing. PDF/A is used for archiving and long-term preservation of electronic documents. The availability of PDF versions depends on the configuration of the print templates.
For more information about PDF/A, please visit https://www.pdfa.org/pdfa-faq/. PDF/A documents generated in ADOGRC are PDF/A-2b compliant.
Image Format for Printing Models to PDF: Set the image format for contained images when printing models to PDF. You can choose between PNG (lossless, bigger size pixel-based image format), JPEG (lossy, smaller size pixel-based image format), and SVG (vector-based image format).
Image Format for Image Generation: Set the image format for generating images (= exporting models in the graphical editor as graphic files). You can choose between PNG (lossless, bigger size pixel-based image format), JPEG (lossy, smaller size pixel-based image format), and SVG (vector-based image format).
Page Limit for Printing Models: Set the maximum number of pages that can be selected in the preview window when printing models to PDF.
Print Templates
The following settings are available:
Default Print Template: Set a default print template for printing models to PDF. When using the ADOGRC Standard Application Library, you can choose between Standard (a minimalistic layout that emphasizes the model image) and Report (a layout based on the standard report for models).
Print Templates Available in Print Dialogue: Define which print templates users can select when printing models to PDF.
Paper Size Settings
Define which paper sizes can be used when printing models to PDF:
Add Paper Size: To add a new paper size, click Add paper size. Then define the format name and the width and height in millimetres (e.g. Letter, 216, 279).
Edit or Delete Paper Size: To the right of the paper size, click
More, and then click Edit or Delete.
System
The system settings allow an ADOGRC administrator to define technical settings controlling the base functionality of ADOGRC.
Open System Settings
To open the system settings:
- Go to Settings > System settings > System.
General Settings
The following settings are available:
- Base URL: This field must contain the URL where ADOGRC can be reached from other machines, ensuring that various ADOGRC features and integrated services work correctly.
What you need to do here depends on the deployment type:
On-premise: Enter the URL in the following format: "
http://<SERVER_NAME>:<TOMCAT_PORT>/ADONIS17_2"<SERVER_NAME>is the hostname or IP address of the Tomcat server,<TOMCAT_PORT>is the HTTP/1.1 Connector Port defined during setup.Base URL Example
You are configuring ADOGRC 14.2 The IP address of the Tomcat server is 10.2.100.68 and you have set Tomcat to use port "8000". The URL should look like this
"
http://10.2.100.68:8000/ADONIS17_2"If you deployed the web application archive
ADONIS17_2.waras the ROOT web application, the URL will be shorter: "http://<SERVER_NAME>:<TOMCAT_PORT>"
SaaS: The Base URL is set automatically during deployment. Do not change this value unless explicitly instructed by BOC Support.
Session timeout (minutes): Specify the number of minutes that a session can remain idle before the server terminates it automatically. The default is 30 minutes.
AJAX timeout for requests from web client to web server (seconds): Enter the timeout for the requests from the web client (= browser) to the web server in seconds.
Technical Users
In this area, you can view and manage technical users. Technical users are used by various components of ADOGRC, for example for the synchronisation of objects with other BOC Management Office products.
The following settings are available:
Select users: Choose the technical users you want from a list featuring all users with the trusted login option enabled.
Remove user: Remove technical users if they are no longer needed.
The ADOGRC application server has to be restarted if these settings are changed. Otherwise the changes will not become effective.
Textual View
The textual view provides a step-by-step guide through a process, allowing users to quickly understand the flow of activities and decisions. It presents models in tabular form, listing objects in rows according to their order in the process, with essential details displayed in the columns.
The availability of the textual view for specific model types depends on the Application Library and product configuration. In the ADOGRC Standard Application Library, this feature is available for Business Process Diagrams by default. ADOGRC administrators can create additional textual view configurations for other model types in the ADOGRC Administration.
Configure Textual View
To edit the textual view settings:
- Go to Settings > Textual view > General.
The textual view configuration wizard has 3 pages:
These pages are discussed in more detail in the following sections.
Select Model Type
The first page of the textual view configuration wizard displays all model types that already have a configuration. Here, you can either modify an existing configuration or create a new one. The following settings are available:
Add Model Type: Click Add model type to select a model type for further editing. Now you can add a configuration for this model type.
Add Configuration: Click Configure to start creating a new configuration for a model type. You will automatically advance to page 2 of the configuration wizard where you can select the object types which should be displayed in the textual view. If a configuration already exists for a model type, the Configure button is replaced by a check mark
.
Active: Select whether the textual view configuration for a specific model type is enabled or disabled. This option is useful if you want to temporarily disable a configuration instead of permanently removing it.
Edit Configuration: To the right of the model type, click
More, and then click Configure to edit an existing configuration. You will automatically advance to page 2 of the configuration wizard where you can select the object types which should be displayed in the textual view.
Delete Configuration: To the right of the model type, click
More, and then click Delete.
After you have completed these settings, select page 2 from the navigation menu at the top to advance to the next page of the textual view wizard.
Select Object Types
The second page of the textual view configuration wizard allows you to select the object types which should be displayed in the textual view. The following settings are available:
Model Types: The model type you've selected to configure is listed here. Adjust it if necessary.
Objects: Select the check boxes next to the object types you want to display in the textual view.
For each object type, you can choose a name attribute and a description attribute to appear in the Name and Description column in the textual view. Additionally, you can select a reference to follow i.e. that in the textual view the link to the properties of the object is replaced by a link to the referenced object/model as selected here.
- Enable bridging: Select this option to display links to subsequent objects in the textual view even when intermediate objects between source object and target object(s) are not shown.
Example: Non-exclusive Gateway
By default, the object type Non-exclusive Gateway is not displayed in the textual view. If Enable bridging is activated, the task that connects to the gateway will point directly to follow-up tasks connected out of the gateway. If bridging is not active, then no links will be displayed.
Order attribute: Select the attribute which is used to order the objects in the model and thus also in the textual view.
Connector relation: Select the relation which is used to connect subsequent objects in a model. By means of this connector relation, links are displayed in the textual view (icon
), which can be used to navigate to the next object(s).
Name attribute: Optional: Select the name attribute of the connector relation. This attribute appears in the textual view to the left of the link to the next object.
After you have completed these settings, select page 3 from the navigation menu at the top to advance to the next page of the textual view wizard.
Select Properties
The third page of the textual view configuration wizard lists all properties that are set to appear in the textual view. Here, you can add or remove properties, and change their position. The following settings are available:
Add Properties: Click Add properties to add new object properties to display in the textual view. They will be added at the bottom of the list, in the order you selected them.
Change Order of Properties: Use the drag handle (
) to drag a property to a new position.
Shown by Default: Select this option to ensure a property is visible by default in the textual view. Clearing this option hides the corresponding column by default, although it can still be made visible as needed.
Used by: Check here to see which object types selected for the textual view use a property.
Remove Property: To the right of the property, click
More, and then click Remove.
After you have completed these settings, click Save. The textual view settings are saved in the database and immediately available in ADOGRC.
Validation
The validation functions in ADOGRC allow ADOGRC users to check whether models and objects comply to the modelling guidelines. If the modelling guidelines are violated, ADOGRC shows corresponding notifications.
ADOGRC provides the following types of checks:
Error,
Warning and
Information: These are programmatic checks that ensure syntactic correctness and proper usage of elements in modelling. Only ADOGRC product developers and customisers can create new checks of these types. However, as an ADOGRC administrator, you can edit these checks. For example, you can modify the text displayed if a check fails or change the category to which a check belongs.
ToDo: These checks serve as reminders for users to manually review and confirm certain conditions. ADOGRC administrators can create new ToDos from scratch and configure them without any restrictions.
Configure Validation
To edit the validation settings:
- Go to Settings > Validation > General.
The validation configuration wizard has 2 pages:
These pages are discussed in more detail in the following sections.
Configure Checks
The first page of the validation configuration wizard presents its content in a table structure containing all checks simultaneously.
Within the editor, checks are sorted alphabetically.
The first table column lists the type of the check (ToDo, Information, Warning, Error).
The second table column contains the name of the check.
The third table column lists the text displayed in the notification.
The fourth table column lists the categories to which a check belongs.
The following options are available:
Add ToDo: Click New ToDo. Now you can configure the check.
Delete Check: To the right of the check, click
More, and then click Delete.
Edit Check: To the right of the check, click
More, and then click Edit, Assign to category or Assign model/object types. Now you can configure the check.
Edit or Add Check
When you add a new ToDo or edit any check on the Configure checks page, a dialogue with three tabs appears. You can view and edit the following data:
Settings
The check's type is listed at the top. Adjust it if necessary.
Next, you can define the content that is displayed if the check is not successful. For every language ADOGRC supports, you can edit the name of the check as well as the text and the hint that are displayed in the notification.
Modifying the type is limited to predefined checks provided with ADOGRC. The type of user-created ToDos is fixed and cannot be altered.
Categories
- Select the categories to which a check belongs. You can also use the search box to quickly find a specific category.
Model/Object Types
- Select the model and object types that will be checked.
For a detailed list of all checks, see Validation Checks Overview.
Reset Values
On any tab, you can select Reset values to restore the default settings for a check.
After you have completed these settings, select page 2 from the navigation menu at the top to advance to the next page of the validation configuration wizard.
Configure Categories
The second page of the validation configuration wizard presents its content in a table structure containing all categories simultaneously.
Every row represents a different category.
The first table column contains the name of the category.
The second table column contains the names of the system roles which are allowed to run checks of this category.
The following options are available:
Add Category: Click New category. Now you can configure the category.
Delete Category: To the right of the category, click
More, and then click Delete.
Edit Category: To the right of the category, click
More, and then click Edit. Now you can configure the category.
Reset Values: To the right of the category, click
More, and then click Reset to restore the default settings for a category.
Assign Checks: To the right of the category, click
More, and then click Assign checks. Now you can select the checks which should belong to this category.
Edit or Add Category
When you add or edit a category on the Configure categories page, a dialogue will appear. You can view and edit the following data:
Name: For every language ADOGRC supports, you can edit the name of the category.
Assign System Roles: Select the system roles which are allowed to run checks of this category.
Extension Module: Lists the extension module which contains the logic for running checks of this category.
Users who execute release workflow transitions need access to the "Release Workflow" category checks. Assign system roles to these users which are allowed to run these checks. These checks are required for the release workflow to work.
For information on which categories are available, see Available Check Categories in the ADOGRC Standard Application Library.
After you have completed these settings, click Save. The validation settings are saved in the database and immediately available in ADOGRC.
Available Check Categories in the ADOGRC Standard Application Library
The following check categories are available if you are using the ADOGRC Standard Application Library:
BPM Best Practice: BPM Best Practice checks ensure the readability, clarity and comprehensibility of models.
BPMN Syntax: BPMN syntax checks assess the model with regard to its syntactic conformity with the BPMN standard and the syntactic rules defined therein.
Layout: Layout checks are used to ensure a uniform appearance.
Methodical: Methodical checks ensure compliance with the methodological guidelines and the integrity of the model portfolio.
Process Architecture: Process architecture checks assess whether the process is anchored in the process architecture.
Process Release Confirmation: This is a checklist of points that should be fulfilled at the latest when the process is released.
Process Structure: These checks ensure that the process meets the required level of detail.
Relation Rules: These checks ensure that relations follow modelling rules.
Release Workflow: Checks within the framework of the model release workflow, which ensure a minimum level of information for release workflow participants and process readers.
For a detailed list of all checks in the various check categories, see Validation Checks Overview.