Configurable Dashboards
With configurable dashboards, you can set up your own personalised digital workspace that brings together key information and metrics relevant to your role. A configurable dashboard serves as a central hub, combining data from different business processes and systems and presenting it in an intuitive, actionable format.
You can view dashboards your colleagues have set up, finding them quickly using the integrated search. Or create your own from scratch, choosing widgets from the widget library and arranging them freely to highlight what matters most, tailoring your workspace to your specific needs and priorities.
The Dashboards Page
The Dashboards page is your starting point for accessing and managing dashboards. Here, all dashboards that have been created are listed, and you can also create new dashboards from scratch.
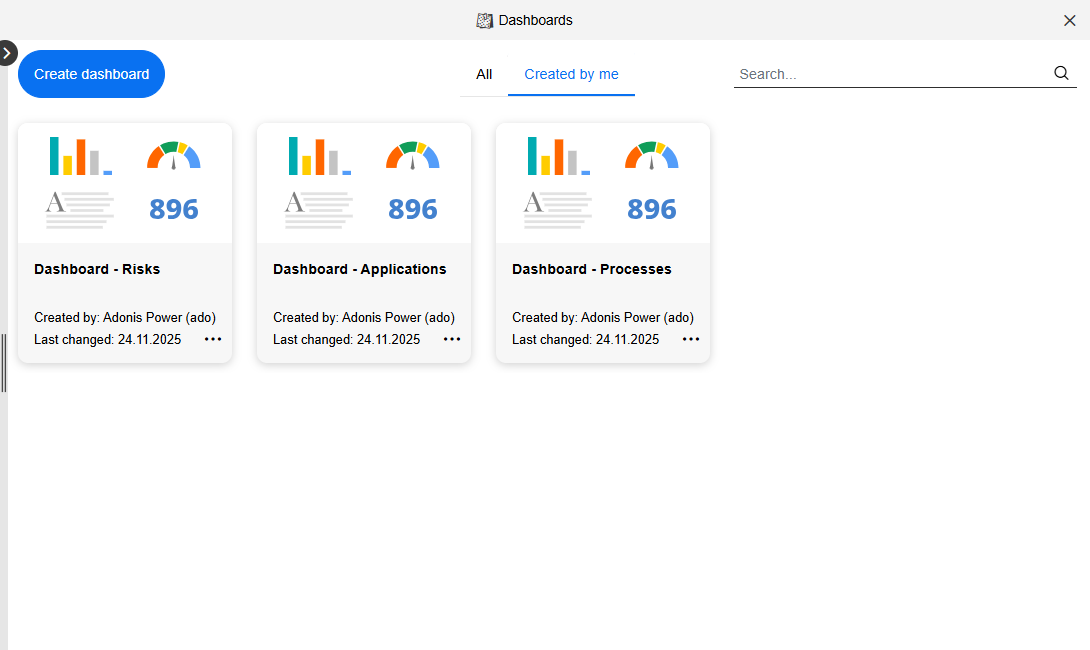
Open Dashboards Page
To open the Dashboards page:
- At the top right of the screen, click
ADONIS Apps, and then select Dashboards.
Create New Dashboard
See Create and Configure Dashboard.
Open a Dashboard
All dashboards are shown as tiles and sorted by date of last change.
- To open a dashboard, click it.
Create and Configure Dashboard
It's easy to create your own dashboards. Here is what you need to do:
Open the Dashboards page.
Set up the new dashboard:
- Click Create Dashboard, enter a meaningful name, and then click Create. The new dashboard opens.
Add and configure widgets to visualise data:
Click + Add widget to open the widget library on the right.
Drag widgets to the dashboard and click
Configure to edit the settings:
Reposition and resize widgets as needed:
Use the drag handle
on the top left to move a widget to a new position.
Use the handle
on the bottom right to adjust the widget size.
Save your dashboard when finished:
- Click Save
For all widgets, text fields such as Title or Description can optionally be translated into all
languages ADONIS supports. Click
Translate next to the field and enter the translations.
Configure Bar Chart
The Bar Chart widget represents data as bars, allowing you to compare values across categories at a glance. The length of each bar is determined by the underlying dataset and the selected aggregation method.
After adding the widget, configure it using the following options (mandatory fields are marked with *):
Title*: Enter a title for the widget.
Description: Provide a short explanation of what the chart displays.
Saved Search*: Select a saved query from the search function in ADONIS: Either a private query you created, or a public one. The search query defines which elements are included in the dataset.
Group by*: Select the property that defines the bars in the chart. You can only choose enumeration attributes or relations that are displayed as columns in the search result.
Show legend: Toggle to show or hide the chart legend.
Value: Defines how the length of each bar is calculated. You have two main options:
Query row count (default): Each bar shows the number of entries in that group.
Attribute aggregation: Select a numeric attribute from the search result for the Value. Bars still represent the groups (e.g., responsible persons), but their lengths now correspond to the aggregated attribute value. Choose the aggregation method Sum, Average, Min, or Max.
Set colours: Choose colours for the bars. You can select them from the colour circles or enter hex values (e.g.
#d62fd6).Chart layout: Choose whether to display the bars vertically or horizontally.
Position of labels: If a horizontal layout is selected, choose whether labels appear inside or outside the bars.
Sort by: Define how bars are sorted. Possible values are Default, Name (ascending), Name (descending), Value (ascending), and Value (descending).
Example: Visualise Risk Distribution
For example, you can create a bar chart based on a saved search for Risks that includes the Responsible Person relation and the Value at Risk attribute as columns. When you select Responsible Person under Group by and Query row count under Value, the bars represent each responsible person, and their lengths show how many risks each person is responsible for (e.g., "Peter Risk" 8, "Carol Process" 5).
If you instead choose Value at Risk for the Value and set the aggregation method to Average, the bars still represent the responsible persons, but now their lengths correspond to the average risk value per person (e.g., "Peter Risk" 40, "Carol Process" 120).
Once you have configured all options, click Save to apply your settings and add the bar chart to the dashboard.
Configure Gauge Chart
The Gauge Chart widget represents data as a single value displayed on a dial, helping you to quickly assess a key metric or status at a glance. It is particularly useful for visualising performance indicators, compliance levels, or other measurable attributes of a specific artefact.
After adding the widget, configure it using the following options (mandatory fields are marked with *):
Title*: Enter a title for the widget.
Description: Provide a short explanation of what the gauge chart displays.
Artefact*: Click + Artefact and select the model or object for which the gauge chart should display data.
Attribute*: Select the enumeration attribute whose value should be shown on the gauge. The pointer on the gauge will indicate the current value of this attribute.
Example: Visualise Application Type
For example, if you select the application "Accounts and Payments System (GIR)" as the artefact and the attribute Application type, the gauge will display the corresponding value, such as No entry, Other, or Database.
Once you have configured all options, click Save to apply your settings and add the gauge chart to the dashboard.
Configure Line Chart
The Line Chart widget represents data as lines, allowing you to visualise changes or trends over time. Each line connects data points derived from a record attribute of a selected artefact.
After adding the widget, configure it using the following options (mandatory fields are marked with *):
Title*: Enter a title for the widget.
Description: Provide a short explanation of what the chart displays.
Artefact*: Click + Artefact and select one or more models or objects whose data you want to display in the line chart.
- Set colours: This option becomes available once one or more columns from the record
attribute have been selected under Y axis. Choose colours for the lines. You can select
them from the colour circles or enter hex values (e.g.
#d62fd6).
- Set colours: This option becomes available once one or more columns from the record
attribute have been selected under Y axis. Choose colours for the lines. You can select
them from the colour circles or enter hex values (e.g.
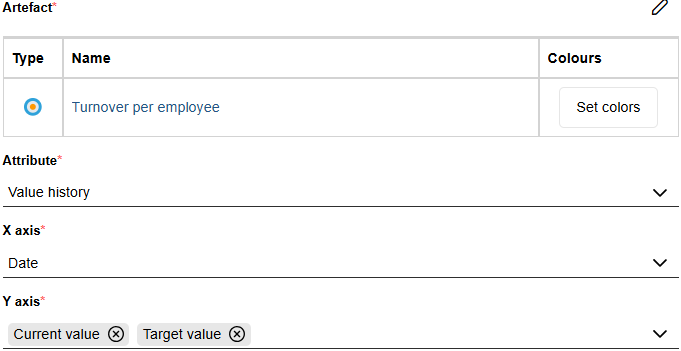
Attribute*: Select a record attribute of the chosen artefact. The attribute must contain structured records, such as historical values or logged measurements. Each record entry represents one data point on the chart.
X axis*: Select the column from the record attribute to be used for the X axis. This typically represents time (for example, Date).
Y axis*: Select one or more columns from the record attribute to be displayed as lines. Each selected column creates one line in the chart (for example, Current value and Target value).
Example: Visualise Performance Indicator Trends
For example, the Performance Indicator object type includes the record attribute Value history, which logs changes in indicator values over time. The attribute contains the columns Current value, Target value, State, and Date. Each time the current value changes, a new entry is created with the associated target value, state, and date.
If you select the Performance Indicator "Turnover per employee" as the artefact, choose Value history as the attribute, Date for the X axis, and both Current value and Target value for the Y axis, the resulting line chart will display two lines over time – one for the current and one for the target value of the performance indicator.
Once you have configured all options, click Save to apply your settings and add the line chart to the dashboard.
Configure Pie Chart
The Pie Chart widget represents data as proportional slices of a circle, allowing you to compare categories as parts of a whole. Each slice corresponds to a category, and its size reflects either the number of entries or the aggregated value.
After adding the widget, configure it using the following options (mandatory fields are marked with *):
Title*: Enter a title for the widget.
Description: Provide a short explanation of what the chart displays.
Saved Search*: Select a saved query from the search function in ADONIS: Either a private query you created, or a public one. The search query defines which elements are included in the dataset.
Group by*: Select the property that defines the slices of the pie. You can only choose enumeration attributes or relations that are displayed as columns in the search result.
Value: Defines how the size of each slice is calculated. You have two main options:
Query row count (default): Each slice represents the number of entries in that group.
Attribute aggregation: Select a numeric attribute from the search result for the Value. The size of each slice corresponds to the aggregated attribute value. Choose the aggregation method Sum, Average, Min, or Max.
Set colours: Choose colours for the slices. You can select them from the colour circles or enter hex values (e.g.
#5cb85c).Sort by: Define how slices are ordered. Possible values are Default, Name (ascending), Name (descending), Value (ascending), and Value (descending).
Example: Visualise Risk Distribution
For example, you can create a pie chart based on a saved search for Risks that includes the Responsible Person relation and the Value at Risk attribute as columns. When you select Responsible Person under Group by and Query row count under Value, each slice of the pie represents a responsible person, and its size shows how many risks each person is responsible for (e.g., "Peter Risk" 80, "Carol Process" 5).
If you instead choose Value at Risk for the Value and set the aggregation method to Average, the slices still represent the responsible persons, but their sizes correspond to the average risk value per person (e.g., "Peter Risk" 40, "Carol Process" 120).
Once you have configured all options, click Save to apply your settings and add the pie chart to the dashboard.
Configure Table
The Table widget displays data in a structured, tabular format. Each row represents a model or object returned by a saved search, and each column corresponds to a property included in that search result.
This widget is ideal for showing detailed information at a glance, such as lists of risks, processes, or applications with key attributes like owner, status, or value.
After adding the widget, configure it using the following options (mandatory fields are marked with *):
Title*: Enter a title for the widget.
Description: Provide a short explanation of what the table displays.
Saved Search*: Select a saved query from the search function in ADONIS: Either a private query you created, or a public one. The elements found by the search are shown as rows, and the properties displayed as columns in the search result also appear as columns in the table.
Example: Display a List of Risks
For example, you can create a table widget based on a saved search for Documents that includes the Referenced document, Document type, and Document author (Responsible person) properties as columns. Each row in the table represents a single document, while the columns show the corresponding values, allowing you to compare and review key document information at a glance.
Once you have configured all options, click Save to apply your settings and add the table to the dashboard.
Configure Text
The Text widget allows you to display arbitrary text on your dashboard. It is useful for notes, instructions, or additional explanations related to other dashboard widgets.
After adding the widget, configure it using the following options (mandatory fields are marked with *):
Title*: Enter a title for the widget.
Description: Provide a short explanation of what the text represents or its purpose.
Text*: Enter the text content to be displayed. You can apply formatting and change the font family, font size, text colour, or make the text bold, italic, etc.
Example: Explain a Chart Widget
You can use a text widget to provide context or explanation for a nearby chart. For instance, place a text widget next to a pie chart showing risk distribution, and enter a short note describing how to interpret the chart slices, what each category represents, or key insights users should notice.
Once you have configured all options, click Save to apply your settings and add the text widget to the dashboard.
Configure Image
The Image widget allows you to display an image on your dashboard. This is useful for logos, illustrations, or any visual content that supports the context of other dashboard widgets.
After adding the widget, configure it using the following options (mandatory fields are marked with *):
Title*: Enter a title for the widget.
Description: Provide a short explanation of the image’s purpose or context.
Image*: Click + Choose and select the image you want to upload. You can also drag a file from your computer to the Drag and drop files here to upload area.
Example: Display a Logo
For instance, you can add your company logo as an image widget at the top of your dashboard to provide branding.
Once you have configured all options, click Save to apply your settings and add the image to the dashboard.
Configure Number
The Number widget highlights a single numeric value on your dashboard. It is ideal for displaying key figures such as the number of processes, applications, or risks matching a saved search.
After adding the widget, configure it using the following options (mandatory fields are marked with *):
Title*: Enter a title for the widget.
Description: Provide a short explanation of what the widget displays.
Saved Search*: Select a saved query from the search function in ADONIS: Either a private query you created, or a public one. By default, the number displayed represents the count of elements returned by this search.
Value: Defines what the widget displays. You have two main options:
Query row count (default): The widget shows the total number of search results.
Attribute aggregation: Choose a numeric attribute from the search result to display an aggregated value (for example, the total or average cost). Choose the aggregation method Sum, Average, Min, or Max.
Set colours: Define the colour in which the number is displayed. You can enter a hex value (e.g.
#007bff).
Example: Show the Total Number of Draft Processes
For example, you can create a number widget based on a saved search for Processes with the filter
condition State = Draft. The widget then displays the total number of draft versions of processes.
To make it visually stand out, you can set the number colour to green (#5cb85c).
Once you have configured all options, click Save to apply your settings and add the number widget to the dashboard.
Manage Dashboards
Configurable dashboards can be edited, deleted, shared, and more.
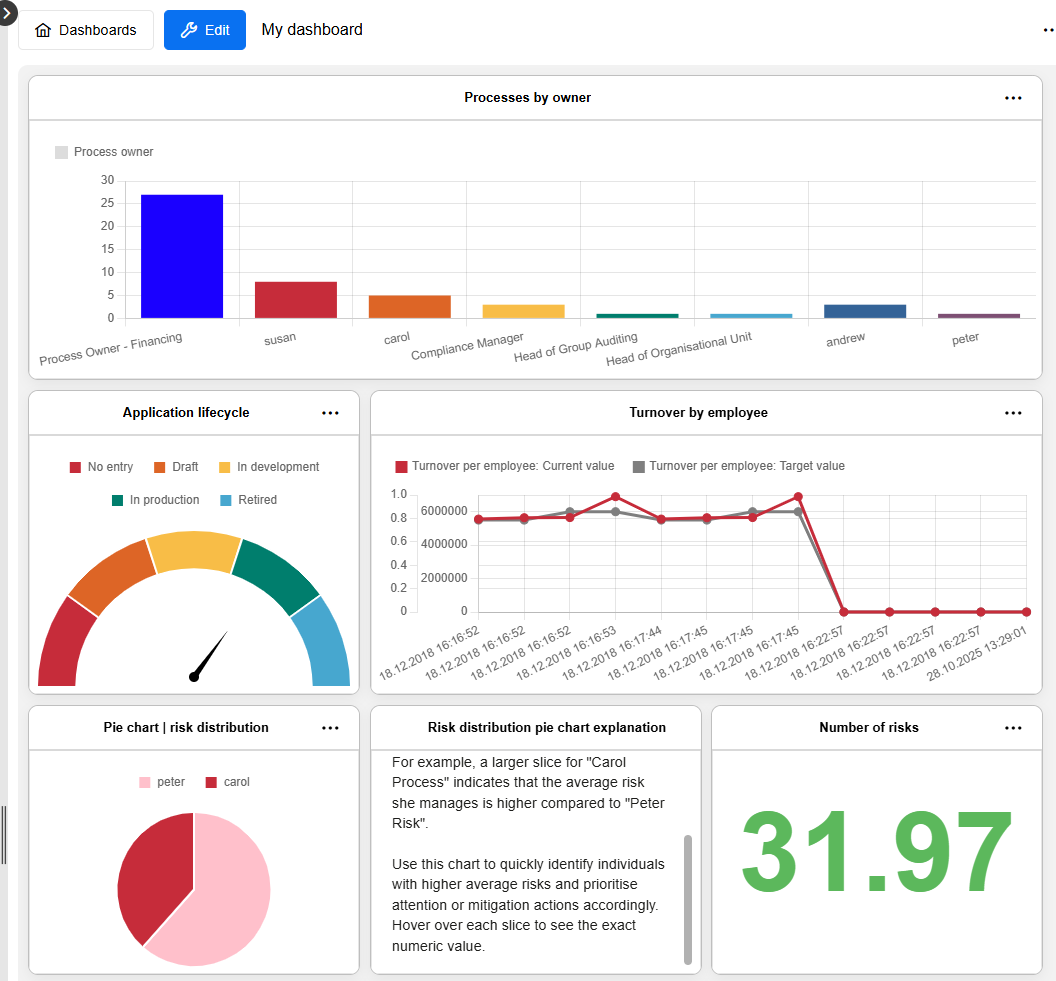
Refresh Dashboard
To update a dashboard so that all widgets display the latest data:
- Click
More at the top right of the dashboard, then select Refresh.
Edit Dashboard
To edit an existing dashboard:
On the Dashboards Page: Click
More on the dashboard tile, and then select Edit. This opens the dashboard in edit mode.
Within an Open Dashboard: Click Edit at the top left of the dashboard to enable edit mode.
Once in edit mode, the following options are available:
Rename Dashboard: Click the pencil icon next to the dashboard name to edit it.
Configure Widgets:
Add, Reposition, and Resize Widgets: Drag widgets from the widget library onto the dashboard, move them using the drag handle
at the top left, and resize using the handle
at the bottom right.
Edit Widget: At the top right of the widget, click
More, and then select Edit to modify the widget configuration.
noteSee Create and Configure Dashboard for more information on configuring widgets.
Delete Widget: At the top right of the widget, click
More, and then select Delete to remove it from the dashboard.
After making your changes, click Save to update the dashboard.
Delete Dashboard
To remove a dashboard that is no longer needed:
On the Dashboards Page: Click
More on the dashboard tile, and then select Delete.
Within an Open Dashboard: Click
More at the top right of the dashboard, then select Delete.
Manage Favourites for Dashboards
To add or remove dashboards as favourites:
- Click Mark as favourite
or Remove from favourites
next to the dashboard name.
Share Dashboard
You can generate a URL for a dashboard. This way you can e.g. easily share it with your colleagues via email.
To generate a URL:
On the Dashboards Page: Click
More on the dashboard tile, and then select Share.
Within an Open Dashboard: Click
More at the top right of the dashboard, then select Share.
Now do one of the following:
Share the URL by email. In the Add people box, start typing the username or email address of a user, and then select the one you want when you see it. If the recipient is not a user or has no email address associated, you need to enter the full email address. Add additional recipients as needed. In the Include a message box, you can add a personal message if you want. When you are done, click Share and the message will be sent.
Paste the URL wherever you need it. Click Copy to directly copy the URL to the clipboard, or copy the URL manually from the Copy link box.
Filter Dashboards
To fine-tune which dashboards are displayed on the Dashboards page:
Select All to display all dashboards (default).
Select Created by me to display only dashboards that you created.
Find Dashboards
To find a dashboard on the Dashboards page:
- In the Search... box, type the text you want to search for.
All dashboards that contain the search string in their name are shown.
Manage Save Location & Permissions
Dashboards are repository objects and can be managed like other objects in ADONIS:
New dashboards are stored in your personal objects folder (
Personal Objects\<username>\Dashboards).Dashboards can be moved to a different object group to change their storage location.
ADONIS administrators can assign permissions at the object group or individual dashboard level to control who can view or edit dashboards.
View Widget Data
You can explore and interact with the data displayed in widgets. The available actions depend on the widget type.
Open Query
For widgets that are based on a saved query (for example, Bar Chart, Pie Chart, Table, or Number), you can open the underlying query to see or refine the dataset:
- At the top right of the widget, click
More, and then select Select query.
The related saved query opens in a new window, allowing you to view the saved query and, if you are its creator, modify it.
Open Properties
For widgets based on model or object data (for example, Line Chart or Gauge Chart), you can open the properties of the related artefact.
- At the top right of the widget, click
More, and then select Open properties.
The properties of the artefact open in a new window.
Interact with Charts
Charts are interactive, allowing you to explore underlying data directly from the dashboard.
Bar Charts: Click a bar to open a tabular view showing all elements in that category.
Pie Charts: Click a slice to open a tabular view showing all elements in that category. You can also click a name in the legend to toggle a slice on or off, removing or re-adding it in the chart view.
Line Charts: Click a data point on a line to open a tabular view showing the artefact whose data the line represents.
Use Table Filters
The Table widget includes column filters that let you drill down into data with precision. To apply filters:
Click the filter icon
in a column header to start building your filter.
Select whether all rules (Match all) or any rules (Match any) must be fulfilled for a row to be displayed.
To build a rule, choose an operator such as Starts with, Contains, or Equals. Then enter the value to search for.
Optionally, click Add rule to include additional filter conditions.
Click Apply to confirm your filter settings.
The table view updates automatically to show only the rows that match your filter criteria.